The Impact of Citizenship Education on Students' Behavior
Keywords:
Citizenship education, aggression, problem-solving skills, randomized controlled trial, seventh-grade students, social-emotional learning, educational interventionAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of a Citizenship Education Program on seventh-grade female students' aggression levels and problem-solving skills in Gachsaran.
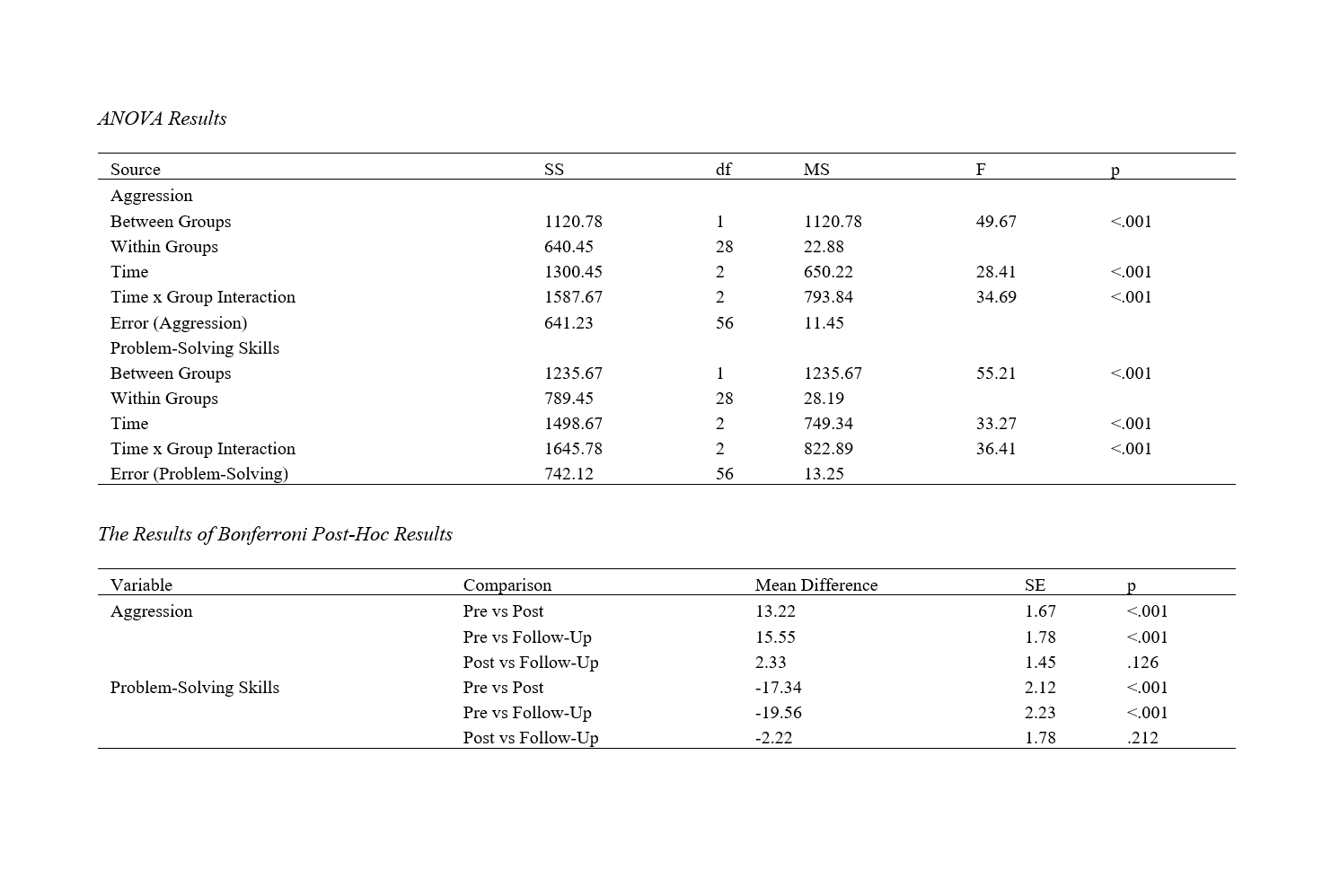
Methods and Materials: This randomized controlled trial involved 30 seventh-grade female students randomly assigned to either an intervention group or a control group, each consisting of 15 participants. The intervention group participated in a Citizenship Education Program consisting of ten 75-minute sessions over ten weeks, while the control group received no intervention. Data were collected using the Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (BPAQ) and the Social Problem-Solving Inventory-Revised (SPSI-R) at three time points: pre-intervention, post-intervention, and five-month follow-up. Data analysis included analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures and Bonferroni post-hoc tests, conducted using SPSS version 27.
Findings: The results indicated a significant reduction in aggression and a significant improvement in problem-solving skills in the intervention group compared to the control group. Descriptive statistics showed that the intervention group's mean aggression score decreased from 45.67 (SD = 5.21) to 32.45 (SD = 4.78) post-intervention, and further to 30.12 (SD = 4.45) at follow-up. Problem-solving skills increased from a mean score of 50.89 (SD = 6.12) to 68.23 (SD = 5.67) post-intervention, and further to 70.45 (SD = 5.78) at follow-up. ANOVA results confirmed significant effects for time, group, and time x group interaction (p < .001). Bonferroni post-hoc tests indicated significant differences between pre-intervention and post-intervention, and pre-intervention and follow-up for both variables.
Conclusion: The Citizenship Education Program significantly reduced aggression and improved problem-solving skills among seventh-grade female students, with sustained effects observed at a five-month follow-up. These findings suggest that integrating citizenship education into the curriculum can effectively enhance students' social-emotional competencies and responsible behavior.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

























