Development of a Model of Students' Subjective Well-Being Based on Attachment Styles, Self-Compassion, and Emotion Regulation Styles with the Mediating Role of Quality of Life
Keywords:
Subjective well-being, attachment styles, self-compassion, emotion regulation styles, quality of lifeAbstract
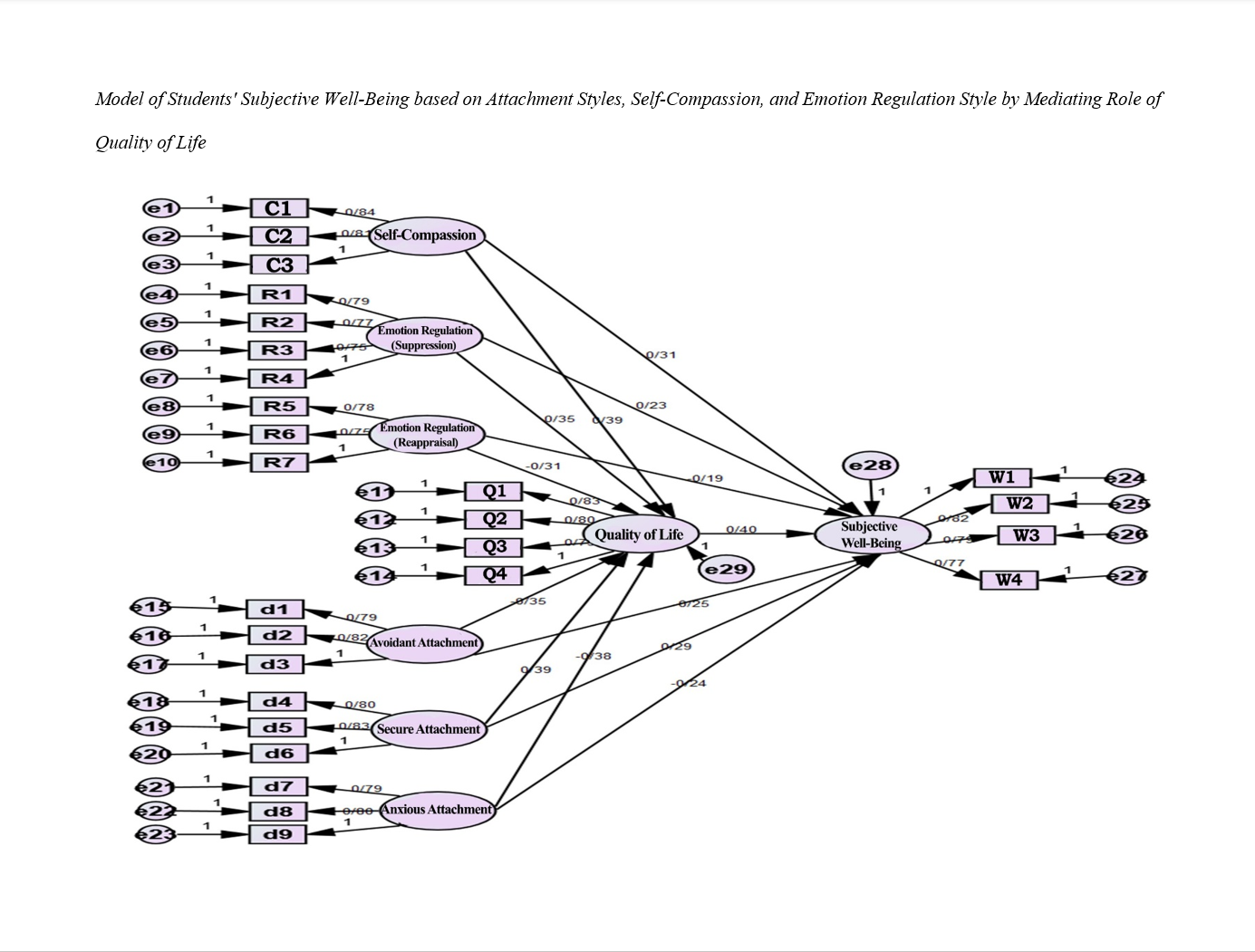
Objective: The aim of the present study was to develop a model of students' subjective well-being based on attachment styles, self-compassion, and emotion regulation styles with the mediating role of quality of life.
Methods and Materials: This study is fundamental in terms of its objective and descriptive-correlational in terms of data collection method. The statistical population of this study included all students of the University of Tabriz in the first semester of the 2023-2024 academic year, approximately 24,000 individuals, from which 378 were selected using a multi-stage cluster random sampling method. To collect information in this study, the following questionnaires were used: the Subjective Well-Being Questionnaire by Molavi et al. (2009), the Adult Attachment Styles Questionnaire by Hazan and Shaver (1987), the Self-Compassion Scale by Neff (2003), the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire by Gross and John (2003), and the World Health Organization Quality of Life Questionnaire (1993). Pearson correlation coefficient and structural equation modeling were used for data analysis.
Findings: The results showed that secure attachment, self-compassion, emotion regulation (reappraisal), and quality of life positively, and anxious attachment, avoidant attachment, and emotion regulation (suppression) negatively, have a direct effect on subjective well-being. Moreover, secure attachment, self-compassion, and emotion regulation (reappraisal) positively, and anxious attachment, avoidant attachment, and emotion regulation (suppression) negatively, have an indirect effect on subjective well-being through quality of life.
Conclusion: Based on the results of this study, it is possible to improve students' subjective well-being by managing the quality of life, even in the presence of insecure attachment styles, insufficient self-compassion, and unhealthy emotion regulation styles.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Melika Rezagholiyan (Author); Fatemeh Nemati (Corresponding Author); Touraj Hashemi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

























