Investigation of the Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Inhibitory Control Deficits and Tendency Toward Stimulant Substance Use in Students
Keywords:
Students, Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation, Inhibitory Control, Stimulants, AddictionAbstract
Objective: This study aims to examine whether transcranial direct current stimulation can effectively improve inhibitory control deficits and reduce students' tendency toward stimulant substance use.
Methods and Materials: This research employed a quasi-experimental design with a pretest-posttest format. The study population included all 12th-grade students with stimulant substance use attending the Atieh Roshan Addiction Treatment Center in Shahriar in 2024. A total of approximately 100 12th-grade students were present at this center. From this population, 40 individuals were selected as the sample, based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, to conduct a targeted study. The statistical population consisted of all 12th-grade students aged 15 to 19 years with stimulant substance use in addiction treatment centers in Shahriar. Multivariate analysis of variance and SPSS26 software were used for data analysis.
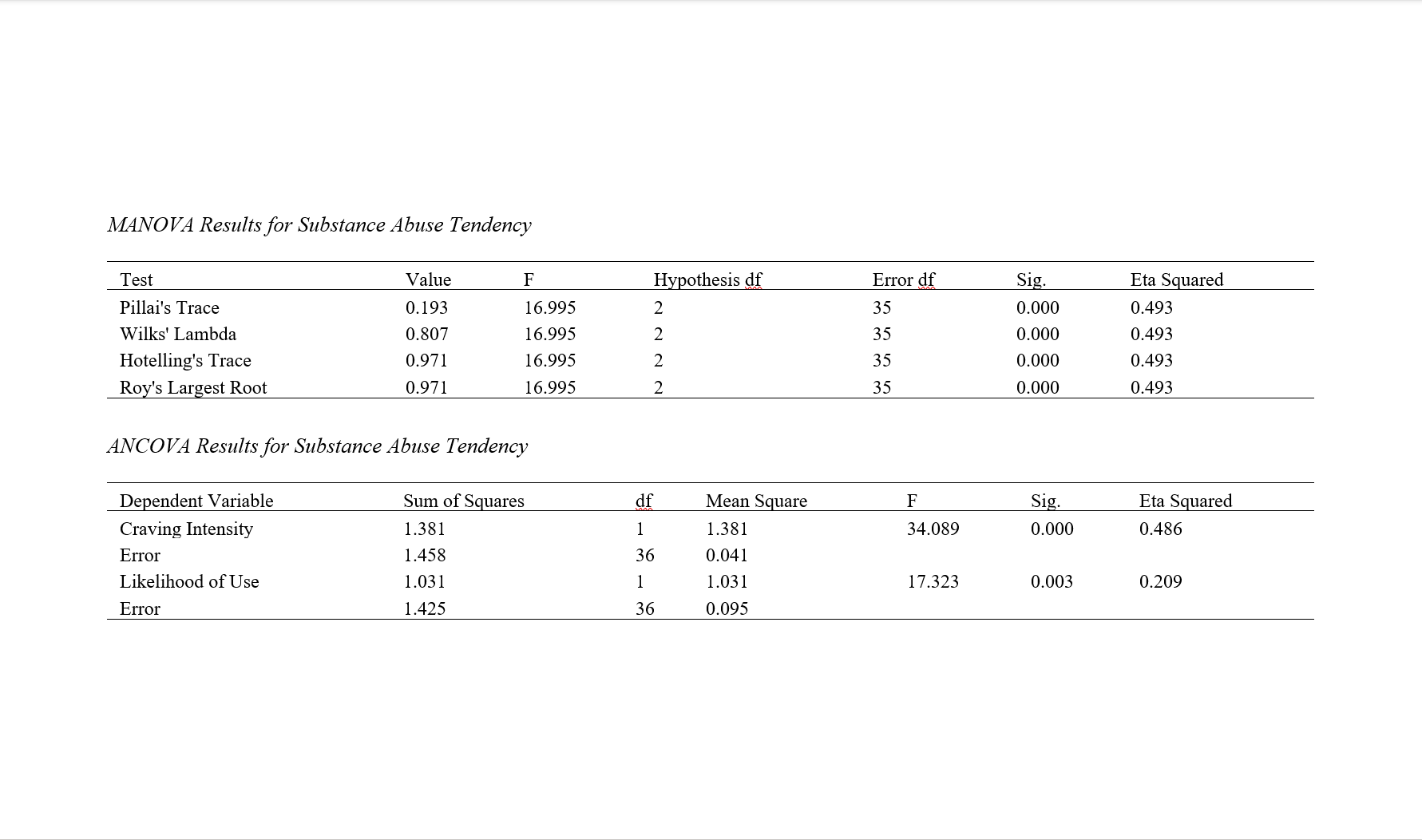
Findings: The results indicated the effectiveness of transcranial brain stimulation on emotional inhibition, aggression inhibition, mental rumination, benign inhibition, and the tendency toward stimulant substance use in students.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that transcranial direct current stimulation can be effective in improving the psychological problems of individuals with substance use disorders.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Babak Sasani (Author); Masoumeh Azemoudeh (Corresponding Author); Hossein Ebrahimi Moghadam, Seyyed Davoud Hoseini Nasab (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








