Media Exposure and Perfectionism: The Mediating Role of Fear of Missing Out
Keywords:
Social media exposure, fear of missing out, perfectionismAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the mediating role of fear of missing out (FoMO) in the relationship between social media exposure and perfectionism among Romanian university students.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was used, and the sample consisted of 380 university students in Romania, selected based on the Morgan and Krejcie table through multi-stage cluster sampling. Participants completed three standardized instruments: the Social Media Use Integration Scale (SMUIS), the Fear of Missing Out Scale (FoMOs), and the Frost Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale (FMPS). Data were analyzed using SPSS-27 for descriptive and Pearson correlation analyses and AMOS-21 for Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to assess direct and indirect relationships among variables. Model fit was evaluated using χ²/df, GFI, AGFI, CFI, TLI, and RMSEA indices.
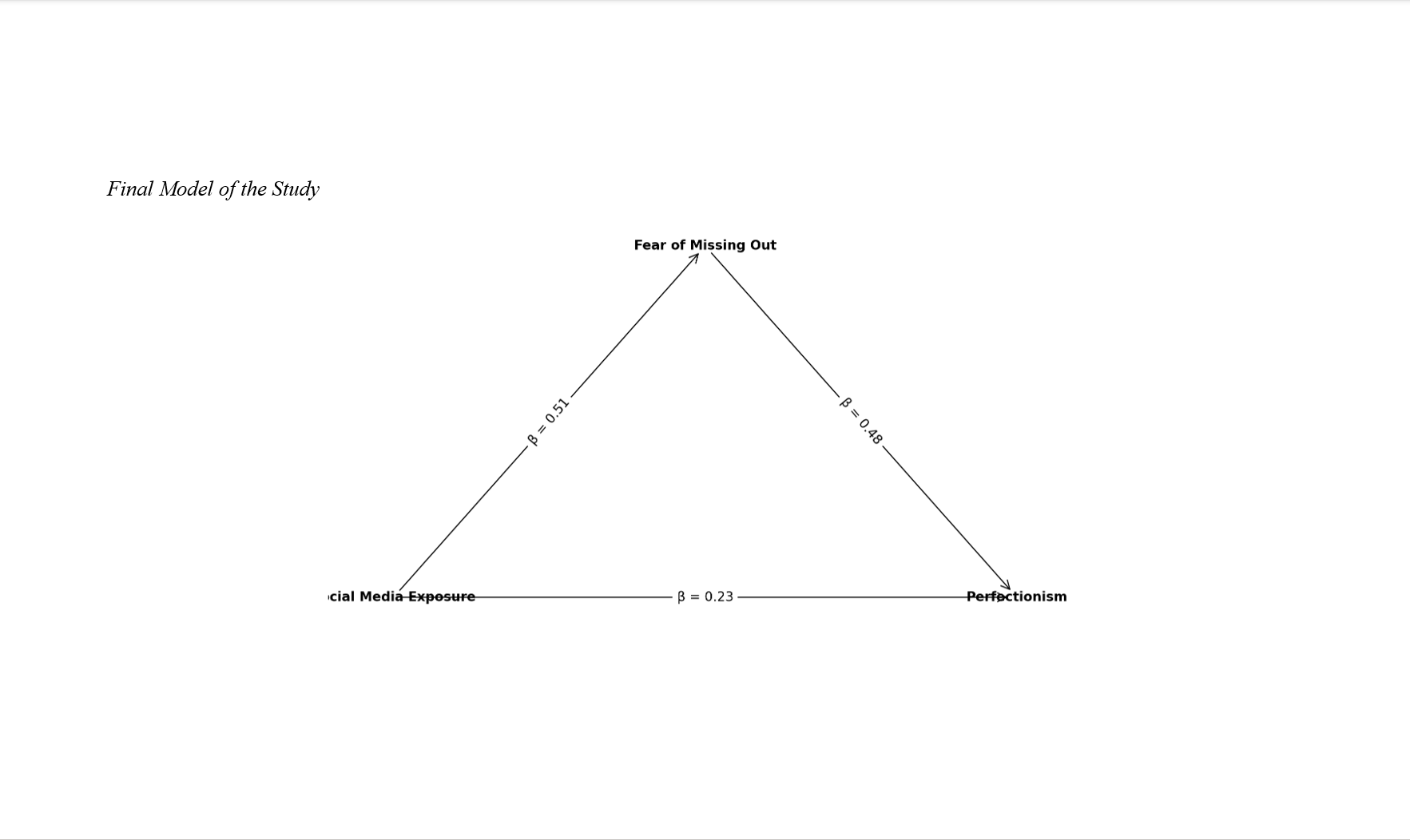
Findings: The results indicated significant positive correlations between social media exposure and FoMO (r = 0.51, p < 0.001), FoMO and perfectionism (r = 0.48, p < 0.001), and social media exposure and perfectionism (r = 0.43, p < 0.001). SEM revealed that FoMO significantly mediated the relationship between social media exposure and perfectionism (β = 0.24, p < 0.001), with a total effect of β = 0.47 (p < 0.001). The model demonstrated excellent fit: χ²/df = 2.07, GFI = 0.94, AGFI = 0.91, CFI = 0.96, TLI = 0.95, and RMSEA = 0.053.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that fear of missing out plays a significant mediating role in linking social media exposure to increased perfectionistic tendencies in young adults. Interventions targeting FoMO may be effective in reducing perfectionism exacerbated by social media engagement.
Downloads
References
Adindu, K. N., Otaniyen, P., Onochie, O. E., Oyedemi, D., Akubuiro, C. O., Nwonye, U. C., & AbdulAzeez, I. M. (2024). The Influence of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health and Substance Abuse Patterns. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 24(2), 253-261. https://doi.org/10.30574/wjarr.2024.24.2.3296
Akbar, B. M. B., Prawesti, D. R. D., & Perbani, W. S. A. (2024). Big Picture Mental Health of Generation Z in the World. Jurnal Kesehatan Komunitas Indonesia, 4(1), 1-20. https://doi.org/10.58545/jkki.v4i1.223
Alfaridzi, G. R., Putri, E. M., & Sulistiasih, S. (2024). Sosial Media Effect Terhadap Mental Health Adolescent Di Tengah Transformasi Digital: Studi Komprehensif Tentang Psikologis Dan Risiko Terkait. Observasi, 2(3), 202-222. https://doi.org/10.61132/observasi.v2i3.491
Aulia, R., & Setiawan, A. (2024). Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media Usage and Mental Health Among Adolescents. Ijss, 1(4), 01-05. https://doi.org/10.62951/ijss.v1i4.140
Beelen, E. v., & Karsay, K. (2024). “The Future Is Bright! Is It?”: Investigating Effects of Hopeful Mental Health Content and Endorsement Cues on Social Media. Social Media + Society, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/20563051241277603
Bell, J. (2025). Public and Mental Health Professionals’ Perspectives on Social Media and Suicide Exposure. BMC public health, 25(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-025-22587-6
Bell, J., & Westoby, C. (2024). Democratised Media and Suicide Prevention: New Implications for Public Health and Policy. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/b7z6j
Bissell, K., & Chou, S. (2024). Living for the Likes: Social Media Use, Fear of Missing Out, and Body and Life Satisfaction in Women. Psychology of Popular Media, 13(3), 481-489. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000507
Campos‐Castillo, C., Groh, S., & Laestadius, L. (2024). Latino Adolescents’ Experiences of Residential Risks on Social Media and Mental Health Implications. Sociology of Health & Illness, 47(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9566.13859
Gu, X., Obrenovic, B., & Wei, F. (2023). Empirical Study on Social Media Exposure and Fear as Drivers of Anxiety and Depression During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability, 15(6), 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065312
Hobiri, M., Adiyati, N., Oktaviany, N., Bintang, M. I., Wahyudi, D., Alvianur, A., Aditya, M., & Putra, M. A. S. (2024). Kritis Terhadap Dampak Media Sosial, Demi Mencegah Turunnya Kualitas Generasi Muda. Globe, 2(4), 294-306. https://doi.org/10.61132/globe.v2i4.674
Holte, A. J., Nixon, A., & Cooper, J. R. (2024). Attachment Anxiety Mediates the Relationship of Need to Belong and Fear of Missing Out (FoMO). Discover Psychology, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44202-024-00250-2
Ibili, G., Tree, J. J., & Gurluk, Y. O. (2025). Maladaptive Perfectionism Can Explain the Inverse Relationship Between Dispositional Mindfulness and Procrastination. PLoS One, 20(2), e0318845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0318845
Jiang, M., Xiao, Y.-W., & Liao, Z. (2024). Pathways of Media Contact to Health Literacy in Middle-Aged and Older People: The Chain Mediation Effect of Perceived Social Support and Self-Efficacy. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, Volume 17, 111-121. https://doi.org/10.2147/jmdh.s448223
Layug, A., Krishnamurthy, S., McKenzie, R., & Feng, B. (2022a). The Impacts of Social Media Use and Online Racial Discrimination on Asian American Mental Health: Cross-Sectional Survey in the United States During COVID-19. Jmir Formative Research, 6(9), e38589. https://doi.org/10.2196/38589
Layug, A., Krishnamurthy, S., McKenzie, R., & Feng, B. (2022b). Social Media Use and Online Racial Discrimination Associated With Negative Psychological Outcomes of Asian Americans and Racial Groups: A Cross-Sectional Survey in the United States During COVID-19 (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.2196/preprints.38589
Mousavi, S. F. (2025). Perfectionism and Burnout in Parents of Visually Impaired Offspring: The Mediating Role of Parenting Conflict and Resilient Coping. Journal of Visual Impairment & Blindness, 119(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145482x251319329
Muhammad, N., Danish, S., & Waqas, M. (2024). The Social Media's Effects Upon Mental Well-Being: Insights From Youth in Pakistani Context. Journal of Social Research Development, 5(2), 349-362. https://doi.org/10.53664/jsrd/05-02-2024-29-349-362
Nugroho, E., Nisa, A. A., Cahyati, W. H., & Najib, N. (2023). Perception, Mental Health, and Social Media Exposure on Adolescents in Indonesia During COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacognosy Research, 11(3), 426-436. https://doi.org/10.56499/jppres22.1560_11.3.426
Obrenovic, B., Godinić, D., Du, G., Khudaykulov, A., & Gan, H. (2024). Identity Disturbance in the Digital Era During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Adverse Effects of Social Media and Job Stress. Behavioral Sciences, 14(8), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080648
Priyana, Y. (2023). The Effect of Social Media Use and Environment on Mental Health Among Young People in Sukabumi. West Science Interdisciplinary Studies, 1(03), 27-33. https://doi.org/10.58812/wsis.v1i03.52
Roshan, I., Ishaque, M., Mohibullah, M., Usman, M., Khilji, Z., Palwasha, & Fatima. (2024). Exploring the Effects of Social Media Exposure on Concentration and Mental Health in Individuals With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Balochistan. JHRR, 4(3), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.61919/jhrr.v4i3.1503
Sao, R., Chandak, S., Barhate, B., & Mondal, S. (2024). Social Media and Gen Z's Mental Well-Being: Impact of Excessive Usage on Anxiety, Stress, and Depression Levels Analysis. Purushartha - A Journal of Management Ethics and Spirituality, 17(1), 23-38. https://doi.org/10.21844/16202117102
Siddiqua, A., Asif, S., & Ain, N. U. (2023). Social Media in the Post-Pandemic World. Global Digital & Print Media Review, VI(I), 10-16. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdpmr.2023(vi-i).02
Sung, Z.-F. (2024). Insight Into the Trends in Research on the Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health. Ieti Transactions on Data Analysis and Forecasting (Itdaf), 2(2), 18-28. https://doi.org/10.3991/itdaf.v2i2.51435
Tera, T., Kelvin, K., & Tobiloba, B. (2024). Influence of Social Media Campaigns on College Students Mental Health Awareness. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/a4beh
Ventriglio, A., Ricci, F., Torales, J., Castaldelli-Maia, J. M., Bener, A., Smith, A., & Liebrenz, M. (2024). Social Media Use and Emerging Mental Health Issues. Industrial Psychiatry Journal, 33(Suppl 1), S261-S264. https://doi.org/10.4103/ipj.ipj_45_24
Vranken, I., Schreurs, L., Noon, E. J., & Vandenbosch, L. (2023). Understanding the Relations Between Exposure to the Positive Self-Portrayals of Others on Social Media and Emerging Adults’ Mental Health During a COVID-19 Imposed Lockdown. Cyberpsychology Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.5817/cp2023-1-5
Yu, Y., Dykxhoorn, J., & Plackett, R. (2024). The Impact of Different Types of Social Media Use on the Mental Health of UK Adults: Longitudinal Observational Study (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.2196/preprints.56950
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








