Impact of Parental Monitoring on Risk Behaviors: The Mediating Role of Moral Identity
Keywords:
Parental Monitoring, Risk Behaviors, Moral Identity, Adolescents, Structural Equation Modeling, ChinaAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the relationship between parental monitoring and adolescent risk behaviors, examining the mediating role of moral identity in this association.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was used with a sample of 414 high school students from China, selected based on the Krejcie and Morgan sample size determination table. Data were collected using three standardized instruments: the Parental Monitoring Scale (Stattin & Kerr, 2000), the Moral Identity Questionnaire (Aquino & Reed, 2002), and the Risk Involvement and Perception Scale (Benthin et al., 1993). Descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated using SPSS-27 to assess bivariate relationships, and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was conducted with AMOS-21 to evaluate direct, indirect, and total effects among the variables and test model fit indices.
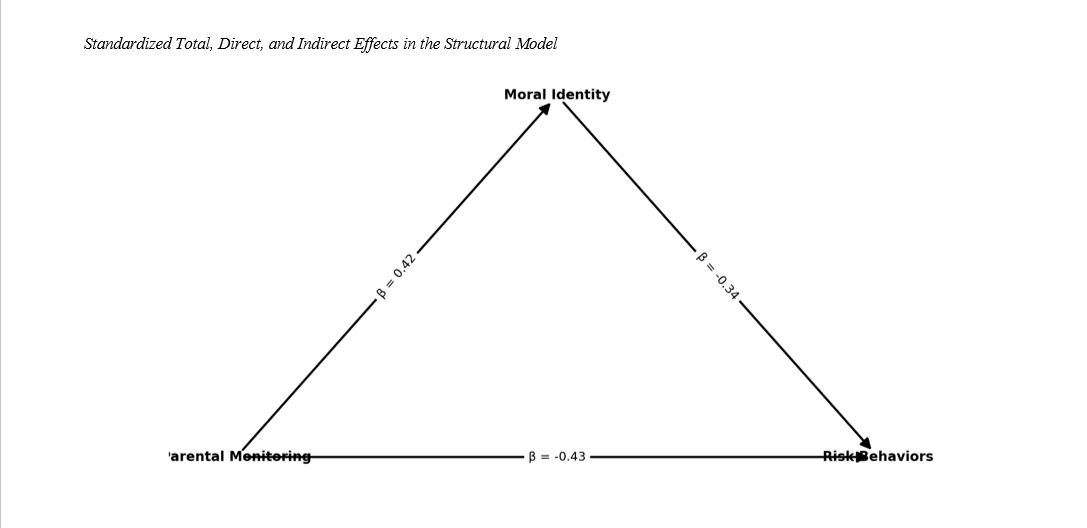
Findings: Descriptive results indicated moderate levels of parental monitoring (M = 35.62, SD = 5.13), moral identity (M = 38.47, SD = 6.29), and relatively low levels of risk behaviors (M = 24.18, SD = 7.64). Pearson correlations revealed significant associations: parental monitoring positively correlated with moral identity (r = .42, p < .001) and negatively with risk behaviors (r = –.51, p < .001); moral identity was also negatively associated with risk behaviors (r = –.47, p < .001). SEM results confirmed that moral identity partially mediated the relationship between parental monitoring and risk behaviors, with a good model fit (χ²/df = 1.97, CFI = 0.96, RMSEA = 0.048). The total effect of parental monitoring on risk behaviors was significant (β = –0.57, p < .001), including both direct (β = –0.43) and indirect effects through moral identity (β = –0.14).
Conclusion: Parental monitoring significantly reduces adolescent risk behaviors both directly and indirectly through the development of moral identity, highlighting the importance of fostering both external regulation and internal value systems in youth.
Downloads
References
Aziz, S., Ajib, M., Razak, A., Nen, S., Manap, J., Hoesni, S. M., & Nasir, M. K. M. (2023). Impact of Parental Monitoring and Communication Factors on Deviant Behavior Among Teenagers in Malaysia. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 58(6). https://doi.org/10.35741/issn.0258-2724.58.6.26
Brooker, R. J., & Buss, K. A. (2014). Harsh Parenting and Fearfulness in Toddlerhood Interact to Predict Amplitudes of Preschool Error-Related Negativity. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 9, 148-159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2014.03.001
Cottrell, L., Rishel, C. W., Lilly, C. L., Cottrell, S., Metzger, A., Ahmadi, H., Wang, B., Li, X., & Stanton, B. (2015). Do Parents Meet Adolescents’ Monitoring Standards? Examination of the Impact on Teen Risk Disclosure and Behaviors if They Don’t. PLoS One, 10(5), e0125750. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125750
Dittus, P., Li, J., Verlenden, J. V., Wilkins, N., Carman-McClanahan, M., Cavalier, Y., Mercado, M. C., Welder, L. E., Roehler, D. R., & Ethier, K. A. (2023). Parental Monitoring and Risk Behaviors and Experiences Among High School Students — Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2021. MMWR supplements, 72(1), 37-44. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.su7201a5
Herman, K. C., Pugh, B., & Ialongo, N. S. (2020). Does Parental Monitoring During Adolescence Moderate Neighborhood Effects on African American Youth Outcomes? Journal of Child and Family Studies, 29(11), 3184-3197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-020-01829-8
Jaggers, J. W., Tomek, S., Hooper, L. M., Mitchell-Williams, M. T., & Church, W. T. (2021). What About the Parental Response?: The Effect of Delinquency and Anger on Parental Monitoring. The Family Journal, 29(3), 316-327. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066480721992511
Jensen-Hart, S., Christensen, J., Dutka, L., & Leishman, J. C. (2012). Child Parent Relationship Training (CPRT): Enhancing Parent-Child Relationships for Military Families. Advances in Social Work, 13(1), 51-66. https://doi.org/10.18060/1881
Junaid, S., Batool, S. S., Nazir, R., & Nayyar, A. (2025). Relationship Between Peer Pressure and Risk Taking Behavior Among Adolescents: Moderating Role of Family Functioning. Res. J. Social Affairs, 3(1), 121-128. https://doi.org/10.71317/rjsa.003.01.0056
Landry, M., Turner, M. M., Vyas, A., & Wood, S. F. (2017). Social Media and Sexual Behavior Among Adolescents: Is There a Link? Jmir Public Health and Surveillance, 3(2), e28. https://doi.org/10.2196/publichealth.7149
Li, P., & Ma, J. (2025). The Influence of Parent-Child Relationship on Prosocial Risk-Taking Behavior in Adolescents: Understanding the Chain Mediating Role of Perceived Social Support and Psychological Capital. Journal of Educational Research and Policies, 7(2), 41-45. https://doi.org/10.53469/jerp.2025.07(02).08
Metzger, A., Ice, C., & Cottrell, L. (2012). But I Trust My Teen: Parents' Attitudes and Response to a Parental Monitoring Intervention. Aids Research and Treatment, 2012, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/396163
Meutuah, R., Afriani, Faradina, S., & Amna, Z. (2023). Predictors of Smoking Intention in Adolescents in Banda Aceh. Insan Jurnal Psikologi Dan Kesehatan Mental, 8(2), 174-194. https://doi.org/10.20473/jpkm.v8i22023.174-194
Rostami, H. A. G., Zeinali, S., Yazdani, A., & ahmadin, z. (2023). Moral Perfectionism and Pro Social Behavior: The Mediating Role of Identity. 1(1), 63-74. https://doi.org/10.34172/srhs.2023.006
Schieber, E., Wang, A., Ou, G., Herbert, C., Nguyen, H. T., Deveaux, L., & Li, X. (2024). The Influence of Socioenvironmental Risk Factors on Risk-Taking Behaviors Among Bahamian Adolescents: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis. Health Psychology and Behavioral Medicine, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/21642850.2023.2297577
Shanti, T. I., & Gryselda, C. D. (2021). Parental Monitoring and Risk Behavior in Middle Adolescents. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 16(3), 356-365. https://doi.org/10.15294/kemas.v16i3.23431
Smith, L., Lynch, K., Driscoll, K. A., & Johnson, S. B. (2021). Parental Monitoring for Type 1 Diabetes in Genetically At‐risk Young Children: The TEDDY Study. Pediatric Diabetes, 22(5), 717-728. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.13173
Suwarni, L., Ismail, D., Prabandari, Y. S., & Adiyanti, M. (2015). Perceived Parental Monitoring on Adolescence Premarital Sexual Behavior in Pontianak City, Indonesia. International Journal of Public Health Science (Ijphs), 4(3), 211. https://doi.org/10.11591/.v4i3.4736
Trucco, E. M., Villafuerte, S., Heitzeg, M. M., Burmeister, M., & Zucker, R. A. (2015). Susceptibility Effects of GABA Receptor Subunit Alpha-2 (GABRA2) Variants and Parental Monitoring on Externalizing Behavior Trajectories: Risk and Protection Conveyed by the Minor Allele. Development and Psychopathology, 28(1), 15-26. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579415000255
Udell, W., Hotton, A., Emerson, E., & Donenberg, G. R. (2017). Does Parental Monitoring Moderate the Impact of Community Violence Exposure on Probation Youth’s Substance Use and Sexual Risk Behavior? Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26(9), 2556-2563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0769-6
Wang, Stanton, Deveaux, Li, X., & Lunn. (2015). Dynamic Relationships Between Parental Monitoring, Peer Risk Involvement and Sexual Risk Behavior Among Bahamian Mid-Adolescents. International Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 41(2), 89. https://doi.org/10.1363/4108915
Wojciechowski, T. (2025). Dual Systems Imbalance as a Predictor of Marijuana Use Risk: Examining Parental Monitoring as a Moderator. Journal of Drug Issues. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220426251326168
Zhang, Y., Cheng, C., Teng, Z., & Guo, C. (2021). Parenting Style and Cyber-Aggression in Chinese Youth: The Role of Moral Disengagement and Moral Identity. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.621878
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








