Structural Equation Modeling of Addiction Proneness in Male High School Students Based on Parental Emotional Tone and Cognitive Bias with the Mediating Role of Coherent Self-Knowledge
Keywords:
addiction proneness, parental emotional tone, cognitive bias, coherent self-knowledge, studentsAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to examine the structural relationships between parental emotional tone and cognitive bias with addiction proneness in male high school students, considering the mediating role of integrative self-knowledge.
Methods and Materials: This correlational study employed a structural equation modeling design. The statistical population included male high school students in Tehran during the 2024–2025 academic year, from whom 590 participants were selected through convenience sampling. Data were collected using the Addiction Proneness Questionnaire, Family Emotional Expressiveness Questionnaire, Cognitive Bias Questionnaire, and Integrative Self-Knowledge Questionnaire. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 26 and AMOS 26. Model fit was evaluated using χ²/df, RMSEA, CFI, GFI, AGFI, NFI, IFI, and SRMR indices. Indirect effects were tested using the bootstrap method.
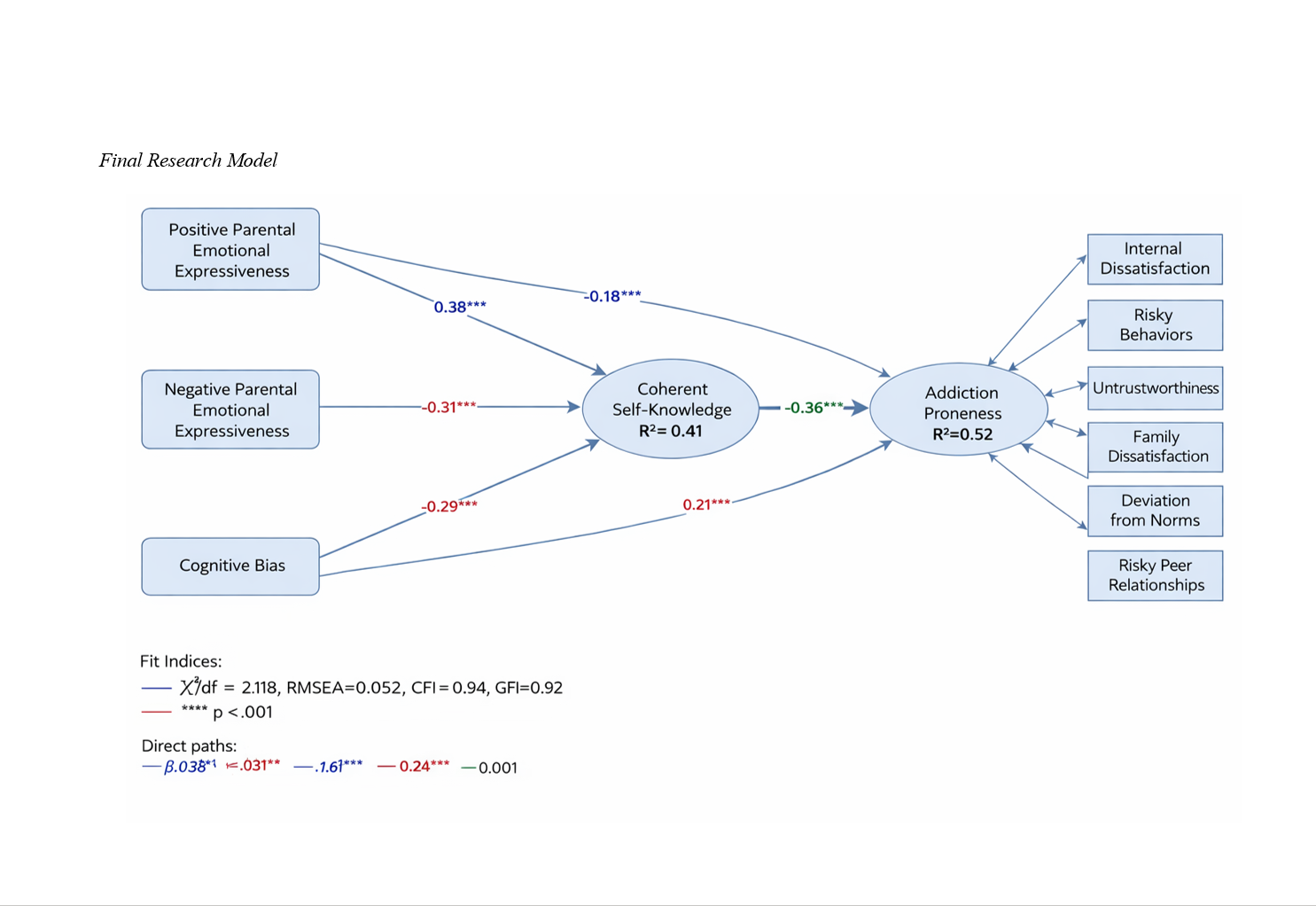
Findings: Positive parental emotional expressiveness had a significant positive effect on integrative self-knowledge (β = 0.38, p < .001) and a significant negative direct effect on addiction proneness (β = −0.18, p < .001). Negative parental emotional expressiveness (β = 0.24, p < .001) and cognitive bias (β = 0.21, p < .001) showed significant positive direct effects on addiction proneness, while both negatively predicted integrative self-knowledge (β = −0.31 and β = −0.29, respectively, p < .001). Integrative self-knowledge significantly reduced addiction proneness (β = −0.36, p < .001) and mediated the relationships between parental emotional tone, cognitive bias, and addiction proneness. The model explained 52% of the variance in addiction proneness and 41% of the variance in integrative self-knowledge, with satisfactory goodness-of-fit indices (χ²/df = 2.18, RMSEA = 0.052, CFI = 0.94).
Conclusion: The findings highlight integrative self-knowledge as a central protective mechanism through which emotional family environments and cognitive processing patterns shape adolescents’ vulnerability to addiction.
Downloads
References
Amini, Z. (2023). Relation of social support status and social health in people with drug abuse. Advanced Biomedical Research, 12(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.4103/abr.abr_85_21
Bauer, P. (2024). Development of self-derivation through memory integration and relations with world knowledge. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/kuchf
Bogdan, R., Hatoum, A. S., Johnson, E. C., & Agrawal, A. (2023). The genetically informed neurobiology of addiction (GINA) model. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 24(1), 40-57. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-022-00656-8
Chang, M. (2024). Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies. PLOS Mental Health, 1(1), e0000022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
Dhakal, S., & Lamsal, R. (2023). Impact of cognitive biases on investment decisions of investors in Nepal. The Lumbini Journal of Business and Economics, 11(1), 35-48. https://doi.org/10.3126/ljbe.v11i1.54315
Dmitrieva, J., & Espel, E. V. (2023). The role of paternal and maternal warmth and hostility on daughter's psychosocial outcomes: The insidious effects of father warmth combined with high paternal hostility. Frontiers in psychology, 14, 930371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.930371
Han, X. (2024). The impact of negative cognitive bias on NSSI: Mediating non-adaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies. BMC Nursing, 23(1). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12912-024-02006-8
Hosseini, J., Shojaeefar, E., Pooladgar, P., Aliakbari, F., Ganji, M., Hamdieh, M., Kheradmand, A., & Fashami, M. A. (2022). Prevalence of substance use among Iranian male adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Science Reports, 5(6), e885. https://doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.885
Howard, T. (2024). Navigating adolescence: Addressing mental health challenges through social work practice and policy. JSWWP, 2(1). https://gexinonline.com/uploads/articles/article-jswwp-108.pdf
Huang, Y. (2024). Investigation of the impact of positive and negative parenting on pre-school and school-aged children's emotion regulation. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 26, 812-818. https://doi.org/10.54097/80sd5a44
Jala, S. (2023). Cognitive bias during clinical decision-making and its influence on patient outcomes in the emergency department: A scoping review. Journal of clinical nursing, 32(19-20), 7076-7085. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16845
Jayte, M., Mohamed, A. A., Karshe, A. H., Ali, H., & Ahmed, A. H. H. (2025). Prescription Drug Misuse and Risk Factors Among Somali Adolescents: A Qualitative Study Exploring Peer Influence, Stress, and Academic Pressure. BMC psychiatry, 25(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-025-07336-8
Lanjekar, P. D., Joshi, S. H., Lanjekar, P. D., Wagh, V., & Wagh, V. (2022). The effect of parenting and the parent-child relationship on a child's cognitive development: A literature review. Cureus, 14(10). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.30574
Marceau, K. (2023). The role of parenting in developmental trajectories of risk for adolescent substance use: A bioecological systems cascade model. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1277419
Mortazavizadeh, Z., Göllner, L., & Forstmeier, S. (2022). Emotional competence, attachment, and parenting styles in children and parents. Psicologia Reflexão E Crítica, 35(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41155-022-00208-0
Muradian, A. A., Timerbulatova, M. F., & Timerbulatov, I. F. (2025). Non-Suicidal Self-Harm and Its Addictive Potential in Adolescents With Drug-Related Disorders. Vestnik Nevrologii Psihiatrii I Nejrohirurgii (Bulletin of Neurology Psychiatry and Neurosurgery)(4), 441-448. https://doi.org/10.33920/med-01-2504-02
Nikstat, A., & Riemann, R. (2022). Differences in parenting behavior are systematic sources of the non-shared environment for internalizing and externalizing problem behavior. Behavior genetics, 53(1), 25-39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-022-10125-8
Rafiee, F. (2023). The Role of Religious Identity in Predicting Internet Addiction and the Tendency towards Drug Use (Case Study: Adolescent Female Students in Pardis, Tehran). Quarterly Journal of New Ideas in Psychology, 16(20). https://jnip.ir/browse.php?a_id=892&sid=1&slc_lang=en
Ramezani, E. (2024). Suicidal tendency and impulsivity and integrative self-knowledge among the adult population. International Journal of High Risk Behaviors and Addiction, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijhrba-137037
Sareen, R. (2022). Cognitive bias in medical decision making. Journal of Pathology Research Reviews and Reports, 1-6. https://doi.org/10.47363/JPR/2022(4)142
Silvers, J. A. (2022). Adolescence as a pivotal period for emotion regulation development. Current opinion in psychology, 44, 258-263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.09.023
Wang, X., He, Y., & Feng, Z. (2022). The antidepressant effect of cognitive reappraisal training on individuals cognitively vulnerable to depression: Could cognitive bias be modified through the prefrontal-amygdala circuits? Frontiers in human neuroscience, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2022.919002
Zhou, L., Cai, E., Chankoson, T., Sukpasjaroen, K., Wu, Y., & Liu, G. (2022). Explaining the relation between perceived social support and psychological well-being among Chinese nursing students: A serial multiple mediator model involving integrative self-knowledge and self-integrity. Psychological Reports, 127(2), 594-619. https://doi.org/10.117