Neural Network Analysis of Adolescent Depression: The Interactive Roles of Loneliness, Family Communication Quality, and Digital Media Dependency
Keywords:
Adolescent depression, neural networks, loneliness, family communication, digital media dependency, mental health modelingAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the nonlinear and interactive effects of loneliness, family communication quality, and digital media dependency on depressive symptoms among Indonesian adolescents using neural network modeling.
Methods and Materials: A cross-sectional design was implemented with 684 secondary school students aged 14–18 years selected via multistage cluster sampling from urban regions of Indonesia. Participants completed validated measures assessing depressive symptoms, loneliness, family communication quality, and digital media dependency. Data were analyzed using a multilayer perceptron neural network constructed in Python with TensorFlow. The dataset was partitioned into training, validation, and test sets. Model performance was evaluated using root mean square error, mean absolute error, and coefficient of determination. Predictor contributions and interaction effects were interpreted using SHAP values and partial dependence analyses.
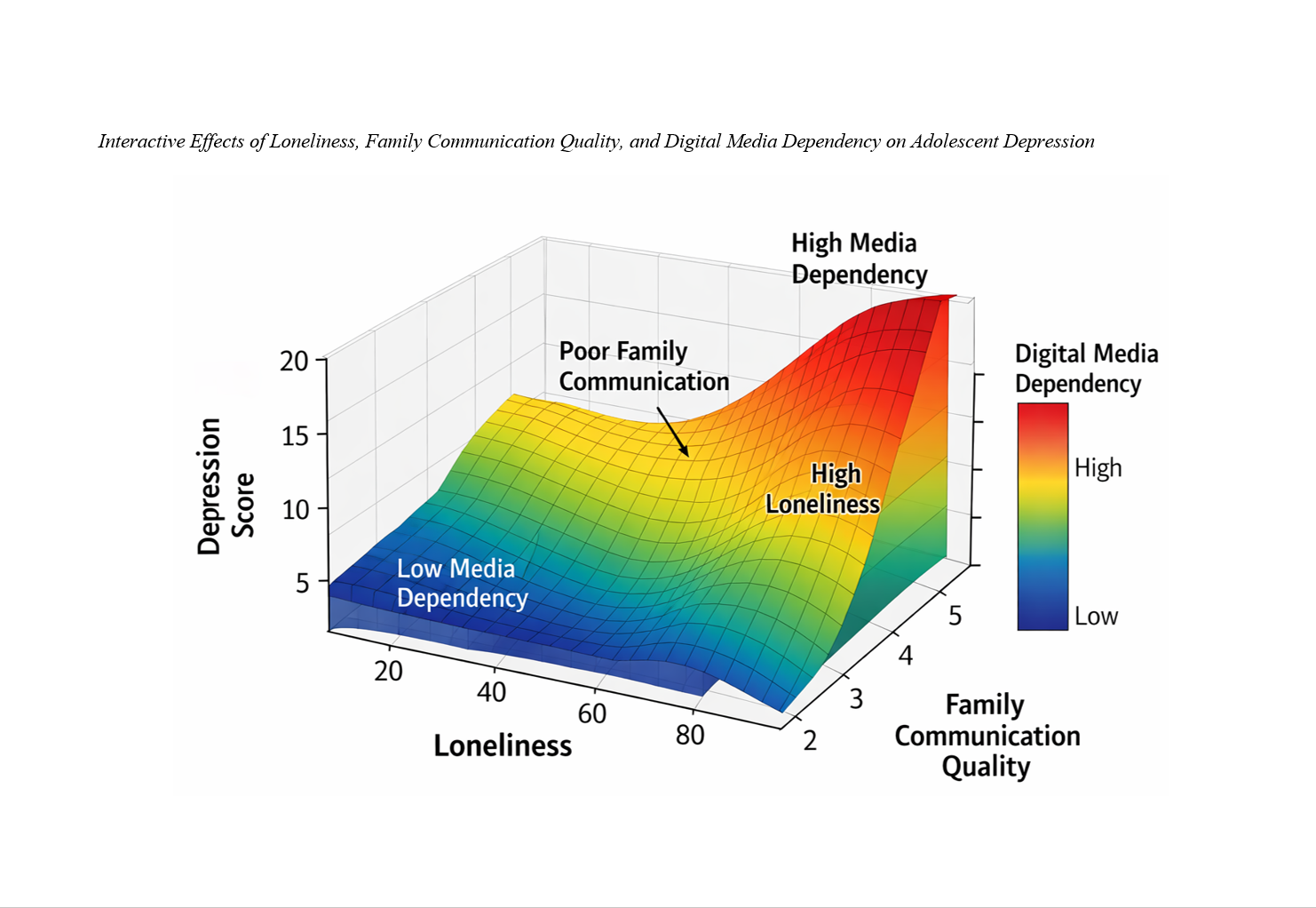
Findings: The neural network demonstrated high predictive accuracy (R² = .79 on the test set). Loneliness emerged as the strongest predictor of depressive symptoms, followed by digital media dependency and family communication quality. Significant nonlinear interaction effects were observed, indicating that the combination of high loneliness, poor family communication, and elevated digital media dependency produced the highest levels of depressive symptoms. Family communication quality exerted a strong buffering effect that attenuated the impact of loneliness and digital dependency on depression.
Conclusion: Adolescent depression is shaped by complex, interactive psychosocial and digital factors that are effectively captured through neural network modeling. Strengthening family communication and promoting healthy digital engagement may substantially reduce depressive risk among adolescents.
Downloads
References
Aldukhail, S. (2025). Relationship Between E-Cigarette Media Content and Product Use: A Scoping Review. Tobacco Induced Diseases, 23(February), 1-20. https://doi.org/10.18332/tid/200547
Alqaderi, N., Elamin, A. B. A., Abdelmonem, K. Y. A., Teir, H. J., & Andrade, G. (2023). Phone Addiction, Cyberbullying, and Mental Health Amongst Young Adults in the United Arab Emirates: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC psychology, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01320-1
Davies, G., Deane, F. P., Williams, V., & Giles, C. (2021). Barriers, Facilitators and Interventions to Support help‐seeking Amongst Young People Living in Families Impacted by Parental Mental Illness: A Systematized Review. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 16(5), 469-480. https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.13194
Dean, L., Buechner, H., Moffett, B. D., Maritze, M., Dalton, L., Hanna, J. R., Rapa, E., Stein, A., Tollman, S., & Kahn, K. (2023). Obstacles and Facilitators to Communicating With Children About Their Parents’ Mental Illness: A Qualitative Study in a Sub-District of Mpumalanga, South Africa. BMC psychiatry, 23(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-023-04569-3
Fitzpatrick, C., Almeida, M. L., Harvey, E. A., Garon‐Carrier, G., Berrigan, F., & Asbridge, M. (2022). An Examination of Bedtime Media and Excessive Screen Time by Canadian Preschoolers During the COVID-19 Pandemic. BMC pediatrics, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-022-03280-8
Gardea-Reséndez, M., Breitinger, S., Walker, A. J., Harper, L., Xiong, A., Stoppel, C., Volety, R., Raman, J., Byun, J. S., Langholm, C., Goes, F. S., Zandi, P. P., Torous, J., & Frye, M. A. (2024). Digital Technologies Tracking Active and Passive Data Collection in Depressive Disorders: Lessons Learned From a Case Series. Journal of Psychiatric Practice, 30(6), 434-439. https://doi.org/10.1097/pra.0000000000000820
Gewali, A., Lopez, A., Dachelet, K., Healy, E., Jean-Baptiste, M., Harridan, H., Evans, Y. N., Unger, J. A., Bhat, A., Tandon, S. D., & Ronen, K. (2021). A Social Media Group Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Intervention to Prevent Depression in Perinatal Youth: Stakeholder Interviews and Intervention Design. Jmir Mental Health, 8(9), e26188. https://doi.org/10.2196/26188
Gong, F., Yi, P., Yu, L., Fan, S., Gao, G., Jin, Y., Zeng, L., Li, Y., & Feei, Z. (2023). Media Use Degree and Depression: A Latent Profile Analysis From Chinese Residents. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1070774
Güveli, R., Balcı, E., & Bayraktar, M. (2024). Nomophobia, Loneliness and Depressive Symptom Levels of Adults Living in a District of Türkiye. Medicine, 103(31), e38921. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000038921
Hilty, D. M., Stubbe, D., McKean, A. J., Hoffman, P., Zalpuri, I., Myint, M. T., Joshi, S. V., Pakyürek, M., & Li, S. T. T. (2023). A Scoping Review of Social Media in Child, Adolescents and Young Adults: Research Findings in Depression, Anxiety and Other Clinical Challenges. BJPsych Open, 9(5). https://doi.org/10.1192/bjo.2023.523
Hong, C., Artur Acelino Francisco Luz Nunes, Q., & Hoskin, J. (2023). The Impact of the COVID‐19 Pandemic on Mental Health, Associated Factors and Coping Strategies in People Living With HIV: A Scoping Review. Journal of the International AIDS Society, 26(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/jia2.26060
Kılınç, A., Çam, C., Ünsal, A., & Arslantaş, D. (2022). Assessment of Nomophobia and Loneliness in Rural Turkish Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Indian Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 18(4), 290-297. https://doi.org/10.1177/09731342231162198
Kouvonen, A., Kemppainen, L., Ketonen, E.-L., Kemppainen, T., Olakivi, A., & Wrede, S. (2021). Digital Information Technology Use, Self-Rated Health, and Depression: Population-Based Analysis of a Survey Study on Older Migrants. Journal of medical Internet research, 23(6), e20988. https://doi.org/10.2196/20988
Kusumota, L., Diniz, M. A. A., Ribeiro, R. M., Iara Lesa Costa da, S., Figueira, A. L. G., Rodrigues, F. R., & Rodrigues, R. A. P. (2022). Impact of Digital Social Media on the Perception of Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older Adults. Revista latino-americana de enfermagem, 30. https://doi.org/10.1590/1518-8345.5641.3526
Lim, M., & Kwon, M. (2023). Factors Influencing Depression in Adolescents Focusing on the Degree of Appearance Stress. Nursing Reports, 13(1), 518-527. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep13010047
Lukenga, M.-P., Billonnet, L., Gaugue, J., & Denis, J. (2023). Exploring Female Students' Perceptions of the Use of Digital Technologies in Managing Academic Stress. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1199038
Malik, M., Rehman, H. K. U., Hussain, A., Hashmi, A., Al-Sunaidar, K. A., Balogh, G. T., Gajdács, M., & Jamshed, S. (2025). Psychological Burden and Coping Strategies Among Pakistani Adults: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study. Epidemiologia, 6(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia6030030
Nesi, J. (2020). The Impact of Social Media on Youth Mental Health. North Carolina Medical Journal, 81(2), 116-121. https://doi.org/10.18043/ncm.81.2.116
Olson, J. A., Sandra, D. A., Veissière, S. P. L., & Langer, E. J. (2023). Sex, Age, and Smartphone Addiction Across 41 Countries. International journal of mental health and addiction, 23(2), 937-945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-023-01146-3
Özbek, M. M., Sevinçok, D., & Mısır, E. (2025). The Relationship Between Familial Functioning and Social Media Use Among Children With Depression and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Comparative Study With Healthy Controls. Children, 12(7), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070906
Roberts, J. A., & David, M. E. (2023). Instagram and TikTok Flow States and Their Association With Psychological Well-Being. Cyberpsychology Behavior and Social Networking, 26(2), 80-89. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2022.0117
Runcan, R., Nadolu, D., & David, G. (2023). Predictors of Anxiety in Romanian Generation Z Teenagers. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(6), 4857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20064857
Sabah, A., Alduais, A., Aljaberi, M. A., & Manouchehri, M. (2025). Online and Offline Social Sensitivity as Mediator Between Online Vigilance and Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Algerian Female Students. PsyCh Journal, 14(4), 473-482. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.70017
Simard, J., & Volicer, L. (2020). Loneliness and Isolation in Long-Term Care and the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 21(7), 966-967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2020.05.006
Sohn, S. Y., Krasnoff, L., Rees, P., Kalk, N. J., & Carter, B. (2021). The Association Between Smartphone Addiction and Sleep: A UK Cross-Sectional Study of Young Adults. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.629407
Song, M. K., Yoon, J. Y., & Kim, E. (2020). Trajectories of Depressive Symptoms Among Multicultural Adolescents in Korea: Longitudinal Analysis Using Latent Class Growth Model. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(21), 8217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17218217
Stiles‐Shields, C., Batts, K. R., Reyes, K. M., Archer, J., Crosby, S., Draxler, J. M., Lennan, N., & Held, P. (2022). Digital Screening and Automated Resource Identification System to Address COVID-19–Related Behavioral Health Disparities: Feasibility Study. Jmir Formative Research, 6(6), e38162. https://doi.org/10.2196/38162
Swartz, H. A., & Novick, D. M. (2020). Psychotherapy in the Digital Age: What We Can Learn From Interpersonal Psychotherapy. American Journal of Psychotherapy, 73(1), 15-21. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.psychotherapy.20190040
Vossen, H. G. M., Regina, J. J. M. v. d. E., Visser, I., & Koning, I. M. (2024). Parenting and Problematic Social Media Use: A Systematic Review. Current Addiction Reports, 11(3), 511-527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-024-00559-x
Vuong, V., Nyman, A. L., Kim, Y., Emery, S., Weaver, S. R., & Huang, J. (2022). Association Between E-Cigarette Advertising Exposure and Use of E-Cigarettes Among a Cohort of U.S. Youth and Young Adults. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(19), 12640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912640
Wei, Y., & Guo, X. (2023). Impact of Smart Device Use on Objective and Subjective Health of Older Adults: Findings From Four Provinces in China. Frontiers in Public Health, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1118207
Wetzel, B., Pryss, R., Baumeister, H., Edler, J.-S., Gonçalves, A. S. O., & Cohrdes, C. (2021). “How Come You Don’t Call Me?” Smartphone Communication App Usage as an Indicator of Loneliness and Social Well-Being Across the Adult Lifespan During the COVID-19 Pandemic. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(12), 6212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126212
Yang, X., Yip, B. H. K., Mak, A. D. P., Zhang, D., Lee, K.-P., & Wong, S. Y. S. (2021). The Differential Effects of Social Media on Depressive Symptoms and Suicidal Ideation Among the Younger and Older Adult Population in Hong Kong During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Population-Based Cross-Sectional Survey Study. Jmir Public Health and Surveillance, 7(5), e24623. https://doi.org/10.2196/24623
Yu, L., & Du, M. (2022). Social Networking Use, Mental Health, and Quality of Life of Hong Kong Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in Public Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1040169