The Effectiveness of Social Problem-Solving Skills Training on Peer Conflict and Social Adjustment in Adolescents
Keywords:
Social problem-solving skills, Peer conflict, Social adjustment, Adolescents, Randomized controlled trialAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to examine the effectiveness of social problem-solving skills training on reducing peer conflict and improving social adjustment among adolescents.
Methods and Materials: This study employed a randomized controlled trial design with an intervention group and a control group. The participants consisted of 30 adolescents from Tehran who were randomly assigned to the intervention (n = 15) and control (n = 15) groups. The intervention group received a structured social problem-solving skills training program delivered in group format over eight weekly sessions, while the control group received no psychological intervention during the study period. Data were collected at three time points: pretest, posttest, and a five-month follow-up. Peer conflict and social adjustment were assessed using standardized self-report instruments with established psychometric properties. Data analysis was conducted using repeated-measures analysis of variance and Bonferroni post-hoc tests with IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.
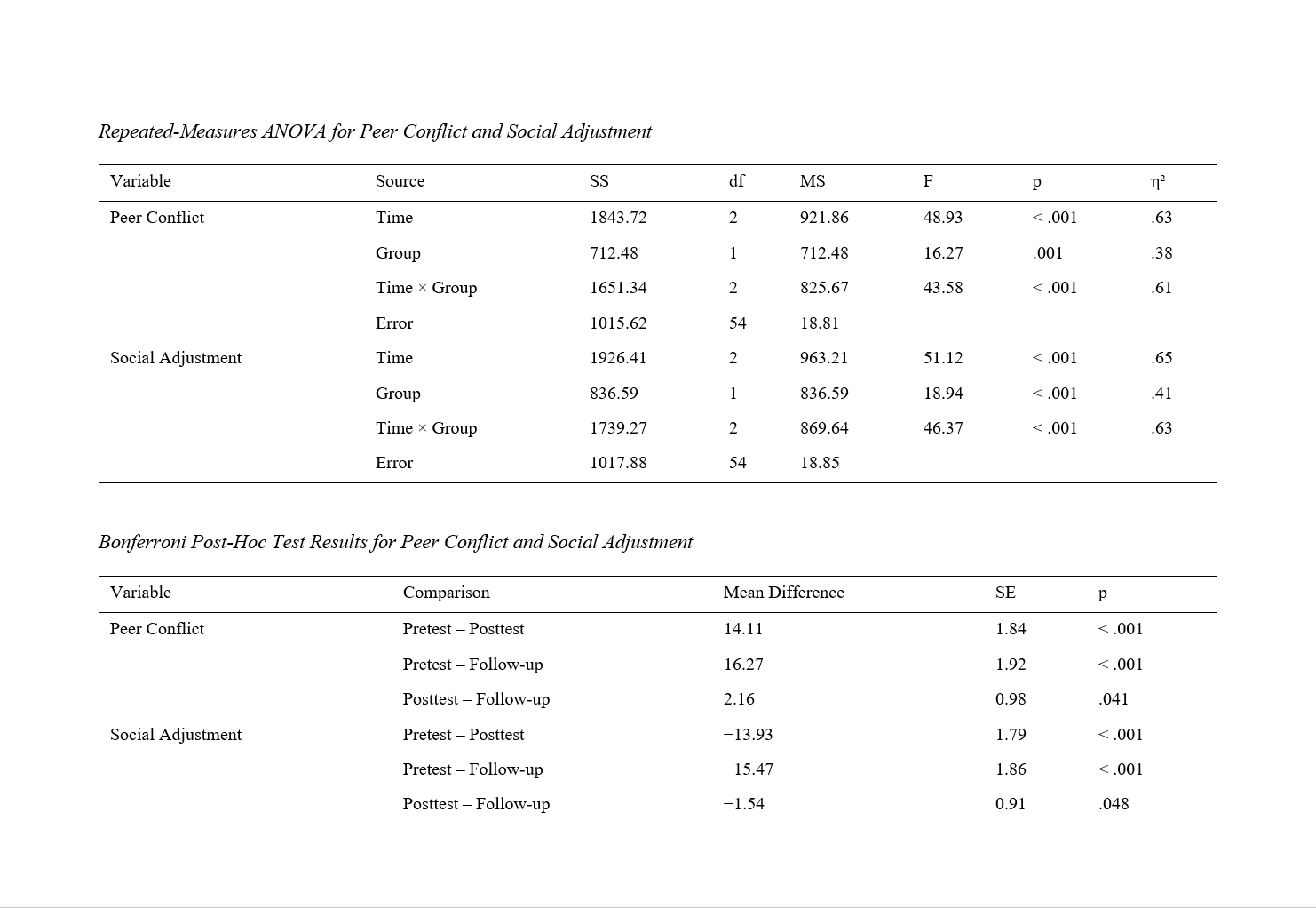
Findings: The results of repeated-measures ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of time and a significant time × group interaction for both peer conflict and social adjustment (p < .001). Adolescents in the intervention group demonstrated a significant reduction in peer conflict scores and a significant increase in social adjustment scores from pretest to posttest, and these improvements were maintained at the five-month follow-up. In contrast, no significant changes were observed in the control group across the three measurement points. Bonferroni post-hoc comparisons confirmed that the differences between pretest and posttest, as well as between pretest and follow-up, were statistically significant for both outcome variables.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that social problem-solving skills training is an effective intervention for reducing peer conflict and enhancing social adjustment among adolescents, with effects that remain stable over time, supporting its use in school-based and preventive mental health programs.
Downloads
References
Apare, J. (2024). Substance Use, Peer Social Comparison, Academic Stress and Psychological Well-Being of Students in Tertiary Institution in Delta South Senatorial District. Asian Research Journal of Arts & Social Sciences, 22(3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.9734/arjass/2024/v22i3518
Gabler, S., Festini, J., Herschmann, L., & Spangler, G. (2025). “Who Am I?”: Identity Development and Psychosocial Adjustment in Foster Adolescents – A Brief Report. Developmental Child Welfare, 7(2-3), 121-136. https://doi.org/10.1177/25161032251324860
Ganotice, F. A., Mendoza, N. B., John Ian Wilzon, T. D., Shen, X., Lee, J. C., Chan, E., Luk, P., Manio, M. M., He, Q., Khoo, U. S., Lam, M. P. S., Chan, S. C. S., Chow, A. Y. M., Wang, N., & Tipoe, G. L. (2024). Students’ Motivation and Engagement in Interprofessional Education: The Mediating Role of Peer Relatedness. Medical Education Online, 29(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2024.2430593
Ghasemi, E., Agharebparast, Z., & Jafari, A. (2024). Effectiveness of Story-Telling on Affective Perspective Taking and Social Problem Solving among Elementary School Girl Students. Journal of early childhood health and education, 5(1), 30-42. https://doi.org/10.32592/jeche.5.1.30
Hassan, S., Zafar, J. M., & Ullah, N. (2024). Effect of Using Problem Solving Technique of 5Es Instructional Model on Student'Learning at Secondary Level: An Analysis. Pakistan Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 12(2), 2279-2289. https://doi.org/10.52131/pjhss.2024.v12i2.2409
Jung, H., & Bae, J. (2024). Good Friends, Better Society: Peer Effects on Civic‐mindedness of Elementary School Students. Children & Society, 39(1), 322-342. https://doi.org/10.1111/chso.12914
Li, Y., Sueb, R., & Hashim, K. S. (2025). The Relationship Between Parental Autonomy Support, Teacher Autonomy Support, Peer Support, and University Students’ Academic Engagement: The Mediating Roles of Basic Psychological Needs and Autonomous Motivation. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1503473
Mam Ghaderi, K., Seyedi Moghaddam, J., Mammeh, A., & Najjari, M. (2024). Determining the Effect Size of Emotional Intelligence and Aggression on Social Adjustment in Sixth-Grade Male Students. Advances in Behavioral Sciences, 9(57), 110-117. http://ijndibs.com/article-1-979-fa.html
Mansi, P. B., & Shraddha, V. (2024). The Influence of Peer Pressure on Students: Cause, Effect, and Strategies for Intervention. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(5). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i05.28091
Moulazadeh, K., & Dasht Bozorgi, Z. (2024). The effectiveness of narrative therapy on emotional intelligence, anger management, and social adjustment in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Caspian Journal of Pediatrics, 10, e5. https://civilica.com/doc/757718/
Nuryana, I. K. D., & Wahyuni, D. (2025). The Role of Learning Motivation in Mediating the Influence of Self-Regulated Learning and Peer Social Support on Academic Burnout in Grade XI Boarding School Students at Madrasah Aliyah, Sleman Regency. Ijems, 2(1), 219-237. https://doi.org/10.61132/ijems.v2i1.451
Özkan, E., & Altuntaş, O. (2024). Effects of online coping skills training on stress, anxiety and social problem solving in young people: A randomised controlled study. International Journal of Social Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1177/00207640241239539
Shao, Y., Kang, S., Lu, Q., Zhang, C., & Li, R. (2024). How Peer Relationships Affect Academic Achievement Among Junior High School Students: The Chain Mediating Roles of Learning Motivation and Learning Engagement. BMC psychology, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01780-z
Tran, T. D., Doan, H. T., Van Pham, T., & Truong, T. M. T. (2024). Social influences, cognitive competence, problem-solving skills: a case study of problem-solving skills in the context of digitalization adoption. International Journal of Instruction, 17(4), 195-218. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2024.17412a
Weisani, M. (2024). The effectiveness of a group social competence training program on social adjustment and anxiety in female students with social anxiety disorder. Ravish Psychology, 13(9), 11-20. https://frooyesh.ir/article-1-5528-en.html
Yacub, A., Drysdale, M., & Callaghan, S. (2024). Challenges of Remote Working, Perceived Peer Support, Mental Health and Well-Being of WIL Students. Education + Training, 66(9), 1165-1182. https://doi.org/10.1108/et-02-2023-0060
Yüksel, A., & Yılmaz, E. B. (2025). Predictors of Peer Bullying and Peer Victimization Among High School Students in Türkiye. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 38(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/jcap.70027
Zafar, J., Tanveer, L., Rashid, M., Shahid, K. S., Sarfraz, L., & Khan, R. M. (2025). Investigating the Impact of Peer Influence on Academic Performance: A Quantitative Cross-Sectional Study Among Medical Students. Jspark, 3(4), 60-65. https://doi.org/10.21649/jspark.v3i4.722
Zhan, Y. (2025). Characterizing Social Problem-Solving Skills in STEAM Activities for Preschool Children. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 2922-2929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2025.01.180
Zhou, T., Luo, Y., Xiong, W., Meng, Z., Zhang, H., & Zhang, J. (2024). Problem-Solving Skills Training for Parents of Children With Chronic Health Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatrics, 178(3), 226-236. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5753
Zhou, X. (2025). The Effect of Peer Relationships on College Students’ Behavioral Intentions to Be Physically Active: The Chain-Mediated Role of Social Support and Exercise Self-Efficacy. PLoS One, 20(5), e0320845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0320845