Explainable AI Analysis of Cognitive Distortions and Their Predictive Role in Adolescent Major Depressive Episodes
Keywords:
Adolescent depression, Cognitive distortions, Explainable artificial intelligence, SHAP analysis, Machine learning, Major depressive episodeAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the predictive role of cognitive distortions in adolescent major depressive episodes using explainable artificial intelligence techniques to enhance both classification accuracy and interpretability of cognitive risk factors.
Methods and Materials: A cross-sectional predictive-correlational design was employed with a sample of 612 adolescents aged 13 to 18 years recruited from secondary schools in Georgia through multistage cluster sampling. Cognitive distortions were assessed using a validated self-report inventory measuring catastrophizing, overgeneralization, personalization, mind reading, and dichotomous thinking. Major depressive episodes were identified using a structured screening protocol based on DSM-5 criteria supplemented by the PHQ-9 adolescent version. Data analysis integrated traditional statistical methods and supervised machine learning algorithms. The dataset was divided into training and testing subsets using stratified sampling. Logistic regression, support vector machine, random forest, multilayer perceptron, and gradient boosting (XGBoost) models were implemented with cross-validation and hyperparameter tuning. Model performance was evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC). Explainability was achieved using SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) to determine feature importance and nonlinear effects.
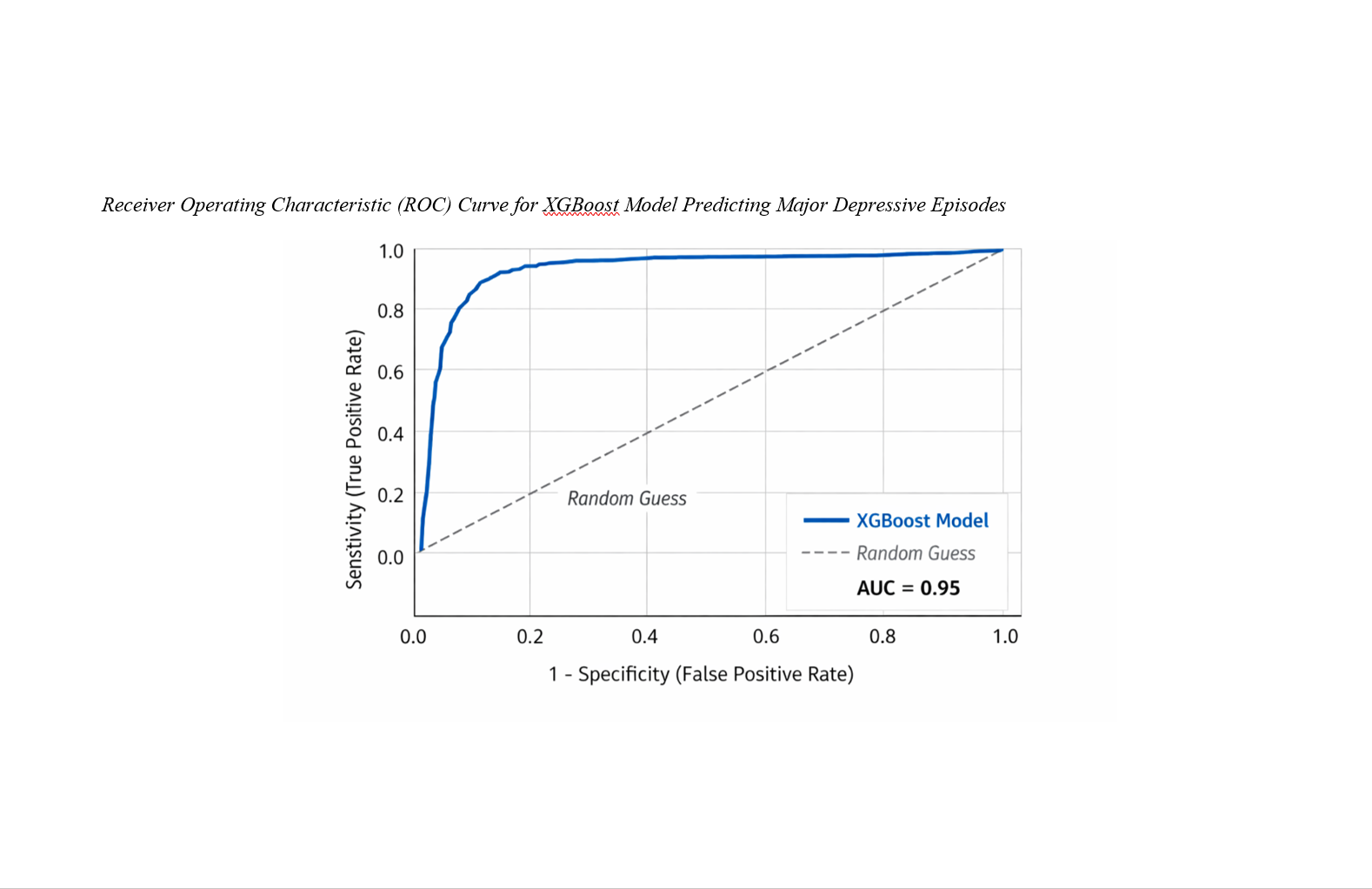
Findings: Cognitive distortions were significantly and positively associated with depressive symptoms (p < 0.01). Machine learning models demonstrated high predictive accuracy, with the XGBoost model achieving the strongest performance (AUC = 0.95). SHAP analysis revealed that catastrophizing, overgeneralization, and mind reading contributed the highest predictive weight to classification outcomes. Nonlinear threshold effects indicated substantially increased depression probability beyond upper-quartile distortion scores.
Conclusion: Cognitive distortions represent powerful and interpretable predictors of adolescent major depressive episodes, and the integration of explainable
Downloads
References
Antosz‐Rekucka, R., & Prochwicz, K. (2025). Pain Sensitivity and Depressive Triad Mediate the Relationship Between Trauma and Stress, and Symptoms of Premenstrual Disorders. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 32(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.70062
Aydin, B. T., & Ay, İ. (2023). Investigating the Relationship Between Bullying Coping Strategies and Cognitive Distortions in Adolescent. International Education Studies, 16(6), 10. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v16n6p10
Azaiez, F., Tannoubi, A., Selmi, T., Quansah, F., Srem‐Sai, M., Hagan, J. E., Azaiez, C., Bougrine, H., Chalghaf, N., Boussayala, G., Ghalmi, I., Lami, M. I., Al-Hayali, M. D. A., Ahmed Wateed Mazyed Shdr, A. L. R., & Al-Sadoon, N. M. N. (2023). Uncovering Cognitive Distortions in Adolescents: Cultural Adaptation and Calibration of an Arabic Version of the “How I Think Questionnaire”. Psych, 5(4), 1256-1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych5040083
Badawy, D. W. B. M. (2023). Psychosocial Factors and Cognitive Distortions Contributing to Self-Reported Quality of Life in Female University Students With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Migration Letters, 21(S1), 72-84. https://doi.org/10.59670/ml.v21is1.5981
Banupriya, N., Neelakandan, S., Prakash, M., & Velmurgan, S. (2025). ERP Insights and Truncated SVD in Conjunction With Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform and Multi-View Hypergraph Neural Networks for Cognitive Distortion Analysis. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-7090487/v1
Bollen, J., Thij, M. t., Breithaupt, F., Barron, A., Rutter, L. A., Lorenzo‐Luaces, L., & Scheffer, M. (2021). Historical Language Records Reveal a Surge of Cognitive Distortions in Recent Decades. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(30). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2102061118
Buğa, A., & Kaya, İ. (2022). The Role of Cognitive Distortions Related Academic Achievement in Predicting the Depression, Stress and Anxiety Levels of Adolescents. International Journal of Contemporary Educational Research, 9(1), 103-114. https://doi.org/10.33200/ijcer.1000210
Chen, Y. (2023). The Relationship Between Working Memory and Depressive Symptoms in Adolescents and Relevant Interventions. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 8, 134-139. https://doi.org/10.54097/ehss.v8i.4238
Dianovinina, K., Surjaningrum, E. R., & Wulandari, P. Y. (2024). Adaptation and Validation of the Children’s Cognitive Triad Inventory for Indonesian Students. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (Ijere), 13(3), 1356. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v13i3.28038
Ebrahimi, S., Moheb, N., & Vafa, M. A. (2024). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy on Cognitive Distortions and Rumination in Adolescents With Social Anxiety Disorder. Practice in Clinical Psychology, 12(1), 81-94. https://doi.org/10.32598/jpcp.12.1.922.1
El-Shokheby, A. M. A. (2020). Investigating the Relationship Between Cognitive Distortions and Academic Stress for Intermediate School Teachers Before and During Work. International Journal of Higher Education, 9(5), 46. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijhe.v9n5p46
Esposito, C., Affuso, G., Dragone, M., & Bacchini, D. (2020). Effortful Control and Community Violence Exposure as Predictors of Developmental Trajectories of Self-Serving Cognitive Distortions in Adolescence: A Growth Mixture Modeling Approach. Journal of youth and adolescence, 49(11), 2358-2371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01306-x
Gomes, H. S., Andrade, J., Ferreira, M., Peixoto, M. M., Farrington, D. P., & Maia, Â. (2021). Measuring Self-Serving Cognitive Distortions With Special Reference to Juvenile Delinquency: A Validation of the “How I Think” Questionnaire in a Sample of Portuguese Adolescents. International journal of offender therapy and comparative criminology, 66(10-11), 1175-1190. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306624x211013544
Ishrat, S., & Naz, S. (2020). Prevalence of Cognitive Distortions Among Adolescents in Punjab, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences Research, 3(01), 195-206. https://doi.org/10.37605/pjhssr.3.1.15
Jaegere, E. D., Heeringen, K. v., Emmery, P., Mommerency, G., & Portzky, G. (2024). Effects of a Serious Game for Adolescent Mental Health on Cognitive Vulnerability: Pilot Usability Study. JMIR serious games, 12, e47513-e47513. https://doi.org/10.2196/47513
Jin, R. (2023). Unraveling Depression: How Modern Pressures Shape Our Minds and Choices. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/uhy85
Marchetti, I., & Pössel, P. (2022). Cognitive Triad and Depressive Symptoms in Adolescence: Specificity and Overlap. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 54(4), 1209-1217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-022-01323-w
Marchetti, I., Pössel, P., & Koster, E. H. W. (2020). The Architecture of Cognitive Vulnerability to Depressive Symptoms in Adolescence: A Longitudinal Network Analysis Study. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 49(2), 267-281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-020-00733-5
Mathieu, S., Barrault, S., Brunault, P., & Varescon, I. (2020). The Role of Gambling Type on Gambling Motives, Cognitive Distortions, and Gambling Severity in Gamblers Recruited Online. PLoS One, 15(10), e0238978. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238978
Mihailescu, I., Efrim-Budisteanu, M., Andrei, L. E., Buică, A., Moise, M., Nicolau, I., Iotu, A., Grădilă, A. P., Costea, T., Priseceanu, A. M., & Rad, F. (2023). Cognitive Coping Strategies Among Inpatient Adolescents With Depression and Psychiatric Comorbidity. Children, 10(12), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121870
Nukhat, A., Salim, A. B. Z., & Shaffie, M. D. F. (2024). Cognitive Distorions and Depression Among Older Adults: Moderating Role of Resilience. Revista De Gestão Social E Ambiental, 18(2), e06893. https://doi.org/10.24857/rgsa.v18n2-127
Özdemir, İ., & Kuru, E. (2023). Investigation of Cognitive Distortions in Panic Disorder, Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Social Anxiety Disorder. Journal of clinical medicine, 12(19), 6351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196351
Özparlak, A., & Karakaya, D. (2022). The Associations of Cognitive Distortions With Internet Addiction and Internet Activities in Adolescents: A Cross‐sectional Study. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 35(4), 322-330. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcap.12385
Primi, C., & Donati, M. A. (2022). The Prevention of Adolescent Problem Gambling Through Probabilistic Reasoning: Evidence of the Intervention’s Efficacy. Canadian Journal of Science Mathematics and Technology Education, 22(3), 591-601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42330-022-00229-y
Rutter, L. A., Edinger, A., Lorenz-Luaces, L., Thiy, M. t., Valdez, D., & Bollen, J. (2024). Anxiety and Depression Are Associated With More Distorted Thinking on Social Media: Longitudinal Observational Study (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.2196/preprints.68338
Rutter, L. A., Edinger, A., Lorenzo‐Luaces, L., Thij, M. t., Valdez, D., & Bollen, J. (2025). Anxiety and Depression Are Associated With More Distorted Thinking on Social Media: A Longitudinal Multi-Method Study. Cognitive therapy and research, 49(4), 712-720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-025-10580-7
Sacco, A., Pössel, P., & Roane, S. J. (2022). Perceived Discrimination and Depressive Symptoms: What Role Does the Cognitive Triad Play? Journal of Clinical Psychology, 79(4), 985-1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.23452
Sağbaş, S. (2025). The Effect of Brief Group Psychoeducation on Cognitive Distortions, Automatic Thoughts and Functioning in Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 32(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.70165
Sapmaz, F. (2023). Relationships Beetween Cognitive Distortions and Adolescent Well-Being: The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience and Moderating Role of Gender. International Journal of Psychology and Educational Studies, 10(1), 83-97. https://doi.org/10.52380/ijpes.2023.10.1.866
Shen, K. (2022). The Dark Triad and Depressive Symptoms Among Chinese Adolescents: Moderated Mediation Models of Age and Emotion Regulation Strategies. Current Psychology, 42(35), 30949-30958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04132-5
Takeda, T., Fukudome, K., Nakano, M., Umehara, H., & Nakamura, K. (2024). Reliability and Validation of the Japanese Version of the Cognitive Distortion Scale. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1261166
Tang, P., Sonuga‐Barke, E., Kostyrka‐Allchorne, K., & Phillips‐Owen, J. (2023). Young People's Future Thinking and Mental Health: The Development and Validation of the Adolescent Future Thinking Rating Scale. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research, 33(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/mpr.1994
Tekin, U., Erermiş, H., Satar, A., Aydın, A. N., Köse, S., & Bildik, T. (2020). Social Cognition in First Episode Adolescent Depression and Its Correlation With Clinical Features and Quality of Life. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 26(1), 140-153. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359104520973254
Thummasorn, S., Ingding, A., Tripheri, P., Janwarn, S., & Jaimuk, A. (2022). The Increases of Cognitive Impairment, Depression Level, and Physical Inactivity in Thai Adolescents With Obese Type 2. Journal of Associated Medical Sciences, 55(3), 60-67. https://doi.org/10.12982/jams.2022.025
Tillerås, K. H., Kjoelaas, S., Dramstad, E., Feragen, K. B., & Lippe, C. v. d. (2020). Psychological Reactions to Predictive Genetic Testing for Huntington’s Disease: A Qualitative Study. Journal of Genetic Counseling, 29(6), 1093-1105. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgc4.1245
Tran, L. C. T. (2025). Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms and Their Determinants Among Adolescents in Can Tho City, Vietnam: A Cross-Sectional Study. Cambridge Prisms Global Mental Health, 12. https://doi.org/10.1017/gmh.2025.10096
Wang, B., Zhao, Y., Lu, X., & Qin, B. (2023). Cognitive Distortion Based Explainable Depression Detection and Analysis Technologies for the Adolescent Internet Users on Social Media. Frontiers in Public Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1045777