Predicting Cyberbullying Perpetration via Random Forest Modeling of Moral Disengagement and Empathy Deficits
Keywords:
Cyberbullying perpetration, Moral disengagement, Empathy deficits, Random Forest, Machine learning, AdolescentsAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to predict cyberbullying perpetration among adolescents using Random Forest modeling of moral disengagement mechanisms and empathy deficits.
Methods and Materials: This cross-sectional quantitative study was conducted among 742 secondary school students (ages 13–18 years) from three provinces in South Africa using multi-stage cluster sampling. Participants completed validated self-report instruments measuring cyberbullying perpetration, moral disengagement, and empathy deficits, alongside demographic indicators and daily internet usage. Data were screened, cleaned, and randomly divided into training (70%) and testing (30%) datasets. A Random Forest classifier with 500 trees was trained to distinguish high versus low cyberbullying perpetration. Hyperparameters were optimized using cross-validation. Model performance was evaluated through accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC). A logistic regression model was estimated as a baseline comparator. Variable importance indices and partial dependence plots were generated to examine predictor contributions and non-linear interaction patterns.
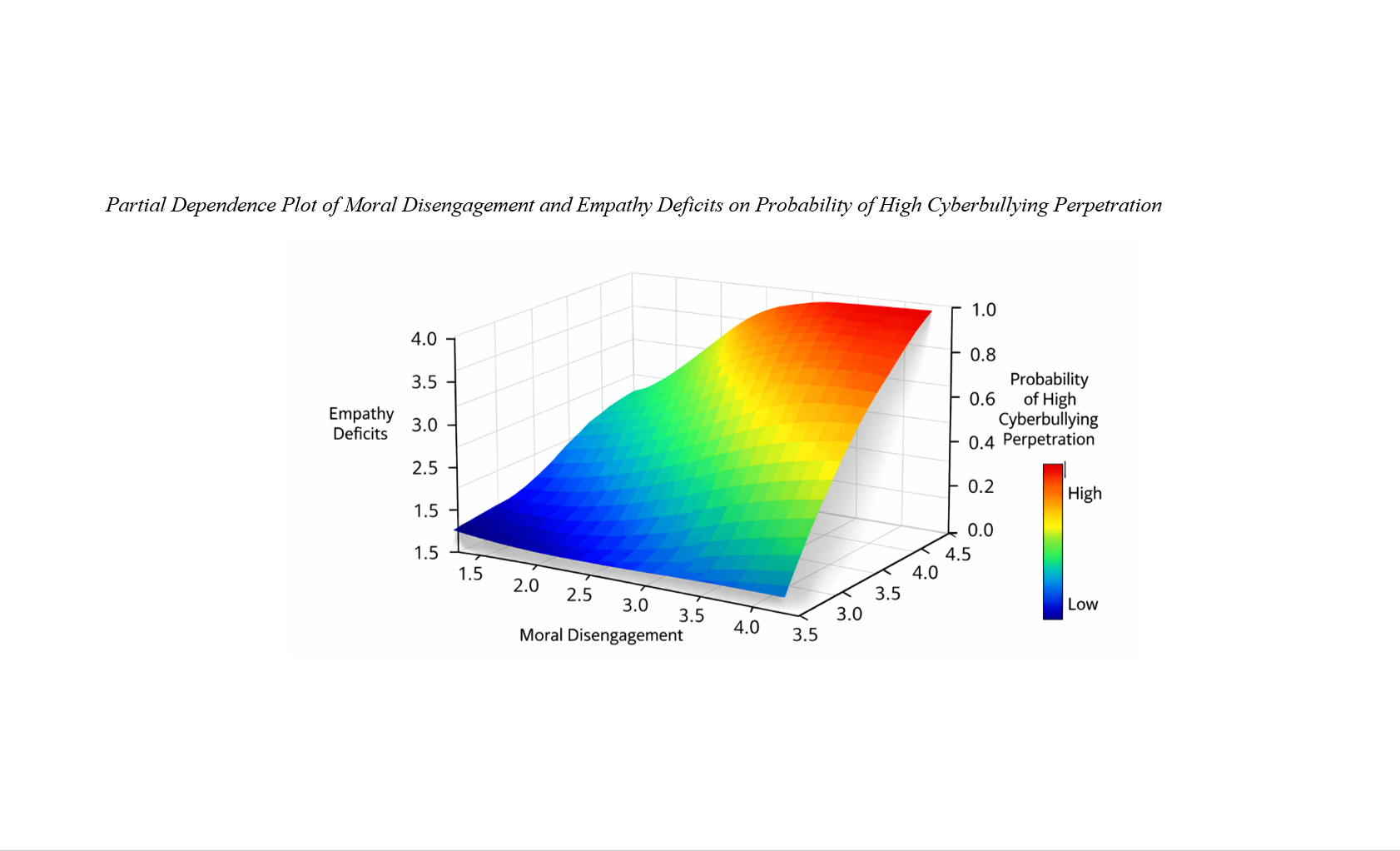
Findings: Inferential analyses indicated that moral disengagement and empathy deficits were significant predictors of cyberbullying perpetration (p < .001). Male students reported higher levels of cyberbullying and moral disengagement (p < .001). The Random Forest model outperformed logistic regression, achieving superior classification accuracy (0.86 vs. 0.74) and AUC-ROC (0.91 vs. 0.78). Variable importance metrics identified overall moral disengagement, dehumanization, and attribution of blame as the strongest predictors, followed by empathy deficits. Partial dependence analysis revealed non-linear threshold effects, with sharp increases in predicted cyberbullying probability at higher levels of moral disengagement, particularly when combined with elevated empathy deficits.
Conclusion: The findings demonstrate that cyberbullying perpetration is most strongly predicted by moral disengagement mechanisms and empathy deficits.
Downloads
References
Abdelaliem, A. (2024). Cyberbullying Motivations and Moral Disengagement Among Adolescent Cyberbullies: Exploring the Mediating Roles. Cyprus Turkish Journal of Psychiatry and Psychology, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.35365/ctjpp.24.1.01
Arató, N., Zsidó, A. N., Lénárd, K., & Lábadi, B. (2020). Cybervictimization and Cyberbullying: The Role of Socio-Emotional Skills. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00248
Bakioğlu, F., Çapan, B. E., Kırteke, S., & Pakpour, A. H. (2024). Adaptation of the Online Moral Disengagement Scale in Turkish: Its Association With Empathetic Tendency and Cyberbullying. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4359069/v1
Castellanos, M., Wettstein, A., Wachs, S., & Bilz, L. (2023). Direct and Indirect Effects of Social Dominance Orientation on Hate Speech Perpetration via Empathy and Moral Disengagement Among Adolescents: A Multilevel Mediation Model. Aggressive Behavior, 50(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.22100
Cheng, C. (2024). Moral Disengagement and the Effect on Cyberbullying Among Adolescents and Young Adults. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 40, 60-63. https://doi.org/10.54097/zttypd29
Concha-Salgado, A., Ramírez, A. M., Pérez, B., Pérez-Luco, R., & Garcı́a-Cueto, E. (2022). Moral Disengagement as a Self-Regulatory Cognitive Process of Transgressions: Psychometric Evidence of the Bandura Scale in Chilean Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(19), 12249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912249
Eden, S., & Landau, O. (2025). Cyberbullying, Moral Disengagement, and Empathy: Exploring Relationship in Children With Behavioral Disorder. Psychology of violence. https://doi.org/10.1037/vio0000631
Falla, D., Romera, E. M., & Ruiz, R. O. (2021). Aggression, Moral Disengagement and Empathy. A Longitudinal Study Within the Interpersonal Dynamics of Bullying. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.703468
Falla, D., Ruiz, R. O., Ferreira, P. C., Simão, A. M. V., & Romera, E. M. (2023). The Effect of Cyberbullying Perpetration on Empathy and Moral Disengagement: Testing a Mediation Model in a Three-Wave Longitudinal Study. Psychology of violence, 13(5), 436-446. https://doi.org/10.1037/vio0000472
Fissel, E. R., Bryson, S. L., & Lee, J. R. (2024). Minimizing Responsibility: The Impact of Moral Disengagement on Cyberbullying Perpetration Among Adults. Crime & Delinquency, 71(10), 3244-3268. https://doi.org/10.1177/00111287241237979
Francisco, S., Ferreira, P. C., Simão, A. M. V., & Pereira, N. (2023). Measuring Empathy Online and Moral Disengagement in Cyberbullying. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1061482
Francisco, S., Ferreira, P. C., Simão, A. M. V., & Pereira, N. (2024). Moral Disengagement and Empathy in Cyberbullying: How They Are Related in Reflection Activities About a Serious Game. BMC psychology, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01582-3
Gajda, A., Moroń, M., Królik, M., Małuch, M., & Mraczek, M. (2022). The Dark Tetrad, Cybervictimization, and Cyberbullying: The Role of Moral Disengagement. Current Psychology, 42(27), 23413-23421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03456-6
Gao, L., Li, X., Wu, X., & Wang, X. (2023). Longitudinal Associations Among Student–student Relationship, Moral Disengagement, and Adolescents’ Bullying Perpetration. School Psychology, 38(5), 337-347. https://doi.org/10.1037/spq0000534
Gómez, A. S., & Durán, N. (2024). Association Between Callous-Unemotional Traits, Empathy, and Moral Disengagement Mechanisms in Juvenile Offenders. Anuario de Psicología Jurídica, 34(2), 85-95. https://doi.org/10.5093/apj2023a7
Günal, B. D., & Ayaz‐Alkaya, S. (2025). Cyberbullying and Empathy Levels in Adolescents and Predictive Factors: A Cross‐Sectional Study. Public Health Nursing. https://doi.org/10.1111/phn.70016
Lan, S., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Hou, X., & Li, C. (2025). From Home to the Screen: How Parental Rejection Fuels Cyberbullying in College Students. PLoS One, 20(5), e0323124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0323124
Ling, G., Li, X., & Wang, X. (2023). Agreeableness and Adolescents' Cyberbullying Perpetration: A Longitudinal Moderated Mediation Model of Moral Disengagement and Empathy. Journal of personality, 91(6), 1461-1477. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12823
Llorent, V. J., Diaz-Chaves, A., Zych, I., Twardowska-Staszek, E., & Marín‐López, I. (2021). Bullying and Cyberbullying in Spain and Poland, and Their Relation to Social, Emotional and Moral Competencies. School Mental Health, 13(3), 535-547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-021-09473-3
Lubis, A. Y., Mikarsa, H. L., & Andriani, I. (2022). Mediation of Moral Disengagement on Cyberbullying Perpetration Influenced by Emotional Intelligence and Anonymity of Indonesian Adolescents on Social Media. Российский Психологический Журнал, 19(4), 231-242. https://doi.org/10.21702/rpj.2022.4.15
Luo, A., & Bussey, K. (2022). Mediating Role of Moral Disengagement in the Perpetration of Cyberbullying by Victims and Bystanders. Journal of adolescence, 94(8), 1142-1149. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12092
Morgan, B., & Fowers, B. J. (2021). Empathy and Authenticity Online: The Roles of Moral Identity, Moral Disengagement, and Parenting Style. Journal of personality, 90(2), 183-202. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12661
Rahmawati, N. P., & Virlia, S. (2023). The Role of Moral Disengagement and Authoritarian Parenting Style Towards Cyberbullying Attitude Among Social Media Users. Jurnal Ilmiah Psikologi Terapan, 11(2), 105-111. https://doi.org/10.22219/jipt.v11i2.25550
Rodríguez‐Hidalgo, A. J., Camargo, V. S., & Hurtado‐Mellado, A. (2025). Cyberbullying Based on Social Stigmas and Social, Emotional and Moral Competencies. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050646
Sorrentino, A., Esposito, A., Acunzo, D., Santamato, M., & Aquino, A. (2023). Onset Risk Factors for Youth Involvement in Cyberbullying and Cybervictimization: A Longitudinal Study. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1090047
Sylvain, E., & Talpade, M. (2024). Exploring the Characteristics of Cyberbullied TikTokers Based on Their Ethnicity. International Journal of Arts Humanities & Social Science, 05(06), 49-53. https://doi.org/10.56734/ijahss.v5n6a8
Tao, R. (2023). Social Cognition and Emotional Response to Bullying Among College Students. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media, 27(1), 206-215. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7048/27/20231188
Tu, Z. C., Cui, Y., Zhang, W., & Luo, F. (2025). Peer Influence and Selection Impact on Adolescent Aggression: Exploring Nonaggressive Delinquency, Peer Victimization, and Moral Disengagement. Journal of adolescence, 97(5), 1344-1359. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12501
Wachs, S., Bilz, L., Wettstein, A., & Espelage, D. L. (2023). Validation of the Multidimensional Bystander Responses to Racist Hate Speech Scale and Its Association With Empathy and Moral Disengagement Among Adolescents. Aggressive Behavior, 50(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.22105
Wachs, S., Bilz, L., Wettstein, A., Wright, M. F., Kansok‐Dusche, J., Krause, N., & Ballaschk, C. (2022). Associations Between Witnessing and Perpetrating Online Hate Speech Among Adolescents: Testing Moderation Effects of Moral Disengagement and Empathy. Psychology of violence, 12(6), 371-381. https://doi.org/10.1037/vio0000422
Wang, L., & Zhou, J. (2023). Violent Video Game Exposure and Cyberbullying in Early Adolescents: A Latent Moderated Mediation Model. Cyberpsychology Behavior and Social Networking, 26(6), 417-424. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2022.0335
Wang, X., Wang, S., & Zeng, X. (2023). Does Deviant Peer Affiliation Accelerate Adolescents' Cyberbullying Perpetration? Roles of Moral Disengagement and Self‐control. Psychology in the Schools, 60(12), 5025-5040. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.23037
Wang, X., Wang, W., Qiao, Y., Ling, G., Yang, J., & Wang, P. (2020). Parental Phubbing and Adolescents’ Cyberbullying Perpetration: A Moderated Mediation Model of Moral Disengagement and Online Disinhibition. Journal of interpersonal violence, 37(7-8), NP5344-NP5366. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260520961877
Xiao, Q., Li, C., Chen, C., & Ma, J. (2025). Whose Prosocial Intentions Are More Affected by Mindfulness, Young Adolescents or Young Adults? PsyCh Journal, 14(6), 912-925. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.70036
Xu, J. (2025). Parental Psychological Control and Cyberbullying Among Adolescents: The Mediating Roles of Sleep Quality and Moral Disengagement and the Moderating Role of Grade. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1664970
Yang, H., Zhang, T., Shi, H.-f., & Fan, C. (2023). Empathy and Bystander Helping Behavior in Cyberbullying Among Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Internet Moral Judgment and the Moderating Role of Internet Self-Efficacy. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1196571
Yang, J., Li, W., Ling, G., & Wang, X. (2020). How Is Trait Anger Related to Adolescents’ Cyberbullying Perpetration? A Moderated Mediation Analysis. Journal of interpersonal violence, 37(9-10), NP6633-NP6654. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260520967129
Zhang, M., & Konishi, C. (2024). Cyberbullying Among Emerging Adults: The Role of Parental Practices and Morality. Journal of Education and Development, 8(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.20849/jed.v8i1.1396