Explainable Machine Learning Prediction of Dropout Risk Using Psychosocial and Cognitive Variables
Keywords:
School dropout, explainable artificial intelligence, machine learning, cognitive functioning, early warning systems, educational risk modelingAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to develop and validate an explainable machine learning model capable of accurately predicting school dropout risk by integrating psychosocial and cognitive variables.
Methods and Materials: A cross-sectional predictive design was employed with a sample of 1.172 secondary school students from three federal states in Germany. Standardized instruments were used to assess psychosocial variables including depressive symptoms, academic self-efficacy, school belonging, teacher and peer support, self-regulation, and academic motivation. Cognitive performance was measured through computerized tasks assessing working memory, processing speed, and fluid reasoning. Socioeconomic status and migration background were included as contextual covariates. Data preprocessing involved multiple imputation, normalization, and class imbalance correction using SMOTE. The dataset was partitioned into training, validation, and independent test subsets. Multiple supervised learning algorithms—logistic regression with elastic net regularization, support vector machines, random forest, and gradient boosting—were trained and compared using cross-validated hyperparameter optimization. Model performance was evaluated using AUC, balanced accuracy, F1-score, and calibration indices. Explainability was ensured through SHAP-based global and local feature attribution analyses.
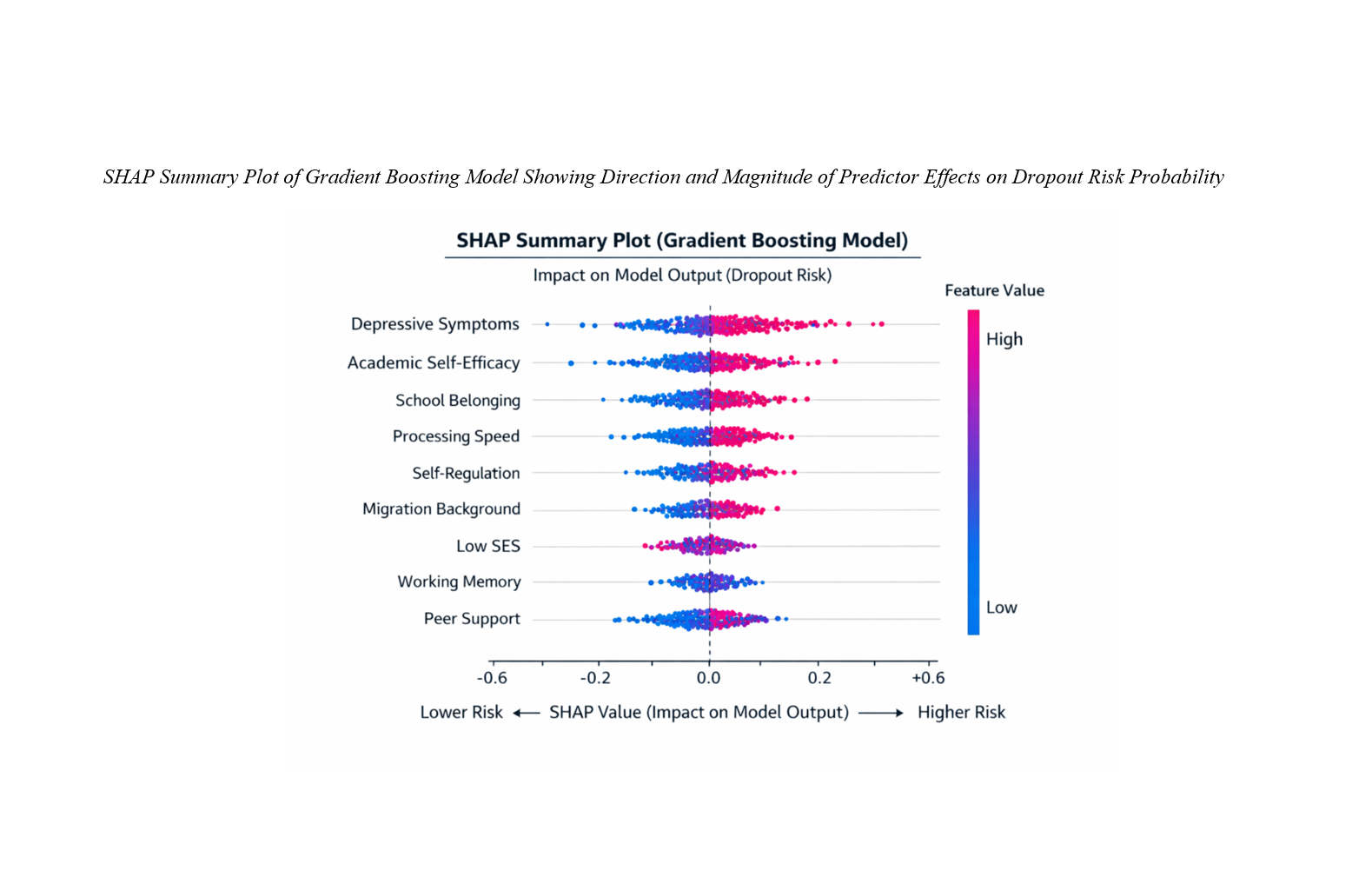
Findings: Gradient boosting achieved the highest predictive performance (AUC = 0.92; balanced accuracy = 0.86), significantly outperforming linear models. Psychosocial variables demonstrated stronger predictive power than cognitive variables alone, yet the integration of both domains significantly improved overall model accuracy. Depressive symptoms, academic self-efficacy, and school belonging emerged as the most influential predictors, while processing speed and working memory provided incremental predictive validity. Nonlinear threshold effects were observed, indicating that elevated emotional distress and reduced cognitive efficiency substantially increased dropout probability.
Conclusion: The findings demonstrate that explainable machine learning models integrating psychosocial and cognitive indicators can reliably predict dropout risk while preserving interpretability.
Downloads
References
Bamicha, V., & Drigas, A. (2024). Strengthening AI via ToM and MC Dimensions. Scientific Electronic Archives, 17(3). https://doi.org/10.36560/17320241939
Cablaida, C. L., & Delfino, A. A. (2025). Building Resilience: Its Implication to SARDO’s Learning Recovery. International Journal of Social Science Humanity & Management Research, 04(06). https://doi.org/10.58806/ijsshmr.2025.v4i6n24
Cahill, S., Hager, R., & Shryane, N. (2023). Patterns of Resilient Functioning in Early Life: Identifying Distinct Groups and Associated Factors. Development and Psychopathology, 36(4), 1789-1809. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579423001165
Christou, A. I. (2025). Neurocognitive and Emotional Outcomes in Childhood Cancer: A Developmental Perspective. Current Oncology, 32(11), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110611
Daud, R. (2024). The Cognitive Benefits of Speaking Multiple Languages. European Journal of Linguistics, 3(4), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.47941/ejl.2055
Demmin, D., Silverstein, S. M., & Shors, T. J. (2022). Mental and Physical Training With Meditation and Aerobic Exercise Improved Mental Health and Well-Being in Teachers During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2022.847301
Gajewski, P. D., Rieker, J. A., Athanassiou, G., Bröde, P., Claus, M., Golka, K., Hengstler, J. G., Kleinsorge, T., Nitsche, M. A., Reinders, J., Tisch, A., Watzl, C., Wascher, E., & Getzmann, S. (2022). A Systematic Analysis of Biological, Sociodemographic, Psychosocial, and Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Work Ability Across the Working Life Span: Cross-Sectional Study (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.2196/preprints.40818
Gajewski, P. D., Rieker, J. A., Athanassiou, G., Bröde, P., Claus, M., Golka, K., Hengstler, J. G., Kleinsorge, T., Nitsche, M. A., Reinders, J., Tisch, A., Watzl, C., Wascher, E., & Getzmann, S. (2023). A Systematic Analysis of Biological, Sociodemographic, Psychosocial, and Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Work Ability Across the Working Life Span: Cross-Sectional Study. Jmir Formative Research, 7, e40818. https://doi.org/10.2196/40818
Galitskaya, V., Drigas, A., & Αντωνίου, Α.-Σ. (2024). Understanding the Challenges of Learning Disabilities and Psychosocial Disorders. Scientific Electronic Archives, 17(6). https://doi.org/10.36560/17620242008
Gooden, J. R., Cox, C. A., Petersen, V., Curtis, A., Sanfilippo, P. G., Manning, V., Bolt, G., & Lubman, D. I. (2022). Predictors of Cognitive Functioning in Presentations to a Community-Based Specialist Addiction Neuropsychology Service. Brain Impairment, 24(1), 54-68. https://doi.org/10.1017/brimp.2021.38
Hausman, H. K., Dai, Y., O’Shea, A., Dominguez, V., Fillingim, M., Calfee, K., Carballo, D., Hernandez, C., Perryman, S., Kraft, J. N., Evangelista, N. D., Etten, E. J. V., Smith, S. G., Bharadwaj, P. K., Song, H., Porges, E. C., DeKosky, S. T., Hishaw, G. A., Marsiske, M., . . . Woods, A. J. (2022). The Longitudinal Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Health Behaviors, Psychosocial Factors, and Cognitive Functioning in Older Adults. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.999107
Jiao, Y. (2025). Deep Learning of Brain-Behavior Dimensions Identifies Transdiagnostic Biotypes in Youth With ADHD and Anxiety Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.10.13.682243
Karageorgopoulos, I., Ανδρικόπουλος, Α., Georgiou, E. S., & Koutsojannis, C. (2025). The Impact and Integration of Biofeedback and Game-Based Learning in Special Education: A Global Perspective on Early Childhood Intervention. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202507.1879.v1
Kira, I. A., Özcan, N. A., Shuwiekh, H., & Alhuwailah, A. (2023). The “Will to Exist, Live and Survive/Fight” (WTELS-F) Scale Initial Short Version: Cross-Cultural Validation of Its Reliability, Structural, Predictive and Incremental Validity. Psychology, 14(03), 470-497. https://doi.org/10.4236/psych.2023.143026
Koblinsky, N., Meusel, L.-A., Greenwood, C. E., & Anderson, N. D. (2021). Household Physical Activity Is Positively Associated With Gray Matter Volume in Older Adults. BMC Geriatrics, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-021-02054-8
Kundu, P. (2025). Artificial Intelligence Modeling of Mood, Coping, Work Engagement and Social Factors in Predicting Mental Health Outcomes. Bio Web of Conferences, 204, 01013. https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/202520401013
Liu, Y. (2025). Directions for Emotional Support in Multicultural Education From a School Violence Prevention Perspective: An Integrative Approach Combining Mindfulness and Counseling. Humanities Meditation Res Inst, 3(2), 41-53. https://doi.org/10.60140/mche.2025.3.2.41
Lupini, F., Rubinstein, T. B., Mackey, E. R., & Sule, S. (2023). Behavioral Health Outcomes and Social Determinants of Health in Children With Diabetes and Juvenile Arthritis. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3610878/v1
Mashar, R., & Astuti, F. P. (2022). Correlation Between Parenting Skills, Children’s Emotional and Intelligence Quotient With School Readiness. Jpud - Jurnal Pendidikan Usia Dini, 16(2), 215-223. https://doi.org/10.21009/jpud.162.02
Mętel, D., Arciszewska, A., Frydecka, D., Cechnicki, A., & Gawęda, Ł. (2020). M65. Interplay of Trait Resilience With Neurocognitive Functioning and Personality Characteristics in Young People With Putative ‘At Risk Mental State’. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 46(Supplement_1), S159-S160. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbaa030.377
Miner-Romanoff, K., & Greenawalt, J. (2024). Evaluation of the Arthur Project: Evidence-Based Mentoring in a Social Work Framework With a Social Justice Approach. Societies, 14(7), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc14070123
Moortel, D. D., Turner, M. C., Arensman, E., Alex Binh Vinh Duc, N., & González, V. M. (2025). Improving Health-Promoting Workplaces Through Interdisciplinary Approaches. The Example of WISEWORK-C, a Cluster of Five Work and Health Projects Within Horizon-Europe. Scandinavian Journal of Work Environment & Health, 51(4), 259-264. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.4238
Morris, E. P., Kraal, A. Z., Levy, S. A., Arias, F., Chen, R., Šeblová, D., Jimenez, M. P., Farina, M., Zlatar, Z. Z., Chanti‐Ketterl, M., Lor, Y., Fletcher, E., Manly, J. J., & Glymour, M. M. (2023). 17 Emotional and Instrumental Support as Protective Factors in Cognitive Aging Among Black and Hispanic/Latinx Older Adults. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 29(s1), 330-331. https://doi.org/10.1017/s135561772300454x
Muhammad, S., & Abdullahi, T. (2025). Post-Traumatic Stress and Academic Adjustment Among Children Affected by Insecurity in Northern Nigeria: Strategies for Psychosocial Intervention in Schools. Federal University Gusau faculty of Education Journal, 5(4), 81-88. https://doi.org/10.64348/zije.202592
Mul, K. (2025). Establishing Biomarkers and Clinical Endpoints in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (END-DM1): Protocol of an International Natural History Study. PLoS One, 20(12), e0331163. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0331163
Nielsen, J., Sharkey, C., Hardy, K. K., & Walsh, K. S. (2023). 11 Social Determinants of Health in Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors: Associations Between Neighborhood Opportunity and Neurocognitive and Psychological Outcomes. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 29(s1), 13-14. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1355617723000942
Rehan, S., & Phillips, N. A. (2023). Social Engagement and Cognitive Decline: Exploring Relationships Between Psychosocial Functioning and Cognitive Performance in Individuals With Mild Cognitive Impairment. Alzheimer S & Dementia, 19(S19). https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.078068
Ribeiro, F. S., & Leist, A. (2023). Risk and Protective Factors for Cognitive Decline in Lower Educated Older Adults With 15‐year Follow‐up. Alzheimer S & Dementia, 19(S8). https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.067868
Sanchez, M. (2025). Neuroscientific Foundations of Early Music Education: Enhancing Cognitive, Emotional, and Social Development in Primary Schools. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, 13(10), 4383-4404. https://doi.org/10.18535/ijsrm/v13i10.el03
Sirois, P. A., Huo, Y., Nozyce, M. L., Garvie, P. A., Harris, L., Malee, K., McEvoy, R. E., Mellins, C. A., Nichols, S., Smith, R., & Tassiopoulos, K. (2022). Ageing With HIV: A Longitudinal Study of Markers of Resilience in Young Adults With Perinatal Exposure to HIV, With or Without Perinatally Acquired HIV. Journal of the International AIDS Society, 25(S4). https://doi.org/10.1002/jia2.25982
Slade, K., Davies, R., Pennington, C. R., Plack, C. J., & Nuttall, H. E. (2022). The Impact of Age and Psychosocial Factors on Cognitive and Auditory Outcomes During the COVID-19 Pandemic. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/rqfjy
Ustinova, О. Y., Zaitseva, N. V., & Eisfeld, D. A. (2022). Substantiating Optimal Parameters of Risk Factors Existing in the Educational Environment for Schoolchildren as Per Indicators of Physical, Mental and Somatic Health. Health Risk Analysis(2), 48-63. https://doi.org/10.21668/health.risk/2022.2.05
Vornyk, B. (2021). Testosterone, Depression, and Cognitive Impairment in Men: An Attempt at Practical Analysis. Health of Man(4), 86-89. https://doi.org/10.30841/2307-5090.4.2021.252406
Warmansyah, J., Ismandela, A., Nabila, D. F., Wulandari, R. T., Wahyu, W. P., Khairunnisa, K., putri, A., Komalasari, E., Sari, M., & Yuningsih, R. (2023). Smartphone Addiction, Executive Function, and Mother-Child Relationships in Early Childhood Emotion Dysregulation. Jpud - Jurnal Pendidikan Usia Dini, 17(2), 241-266. https://doi.org/10.21009/jpud.172.05
Yan, X., Feng, Z., Zhang, H., Zhou, T., Yu, X., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Dynamic Functional Connectivity Changes Associated With Psychiatric Traits and Cognitive Deficits in Cushing’s Disease. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2489663/v1
Yang, C., Pi, Y., Wang, W., Huang, Y., Tang, N., Wang, H., & Wen, S. (2025). Evaluating the Efficacy of Three Classical EEG Paradigms in the Discrimination of Bipolar Depression. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1545132
Яновська, С. Г., & Perelygina, L. (2025). Peculiarities of Resilience and Coping Strategies of the Ukrainian Civilian Population During the Full-Scale War: The Role of Social Support. Visnyk of v N Karazin Kharkiv National University a Series of Psychology(78), 46-52. https://doi.org/10.26565/2225-7756-2025-78-07