Development of a Structured Intervention and Its Effectiveness on High-Risk Behaviors in Substance-Using Adolescents
Keywords:
Adolescence, Substance use, High-risk behaviors, Structured intervention, Mixed-methods designAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to develop a structured, developmentally informed intervention and to examine its effectiveness in reducing high-risk behaviors among substance-using adolescents.
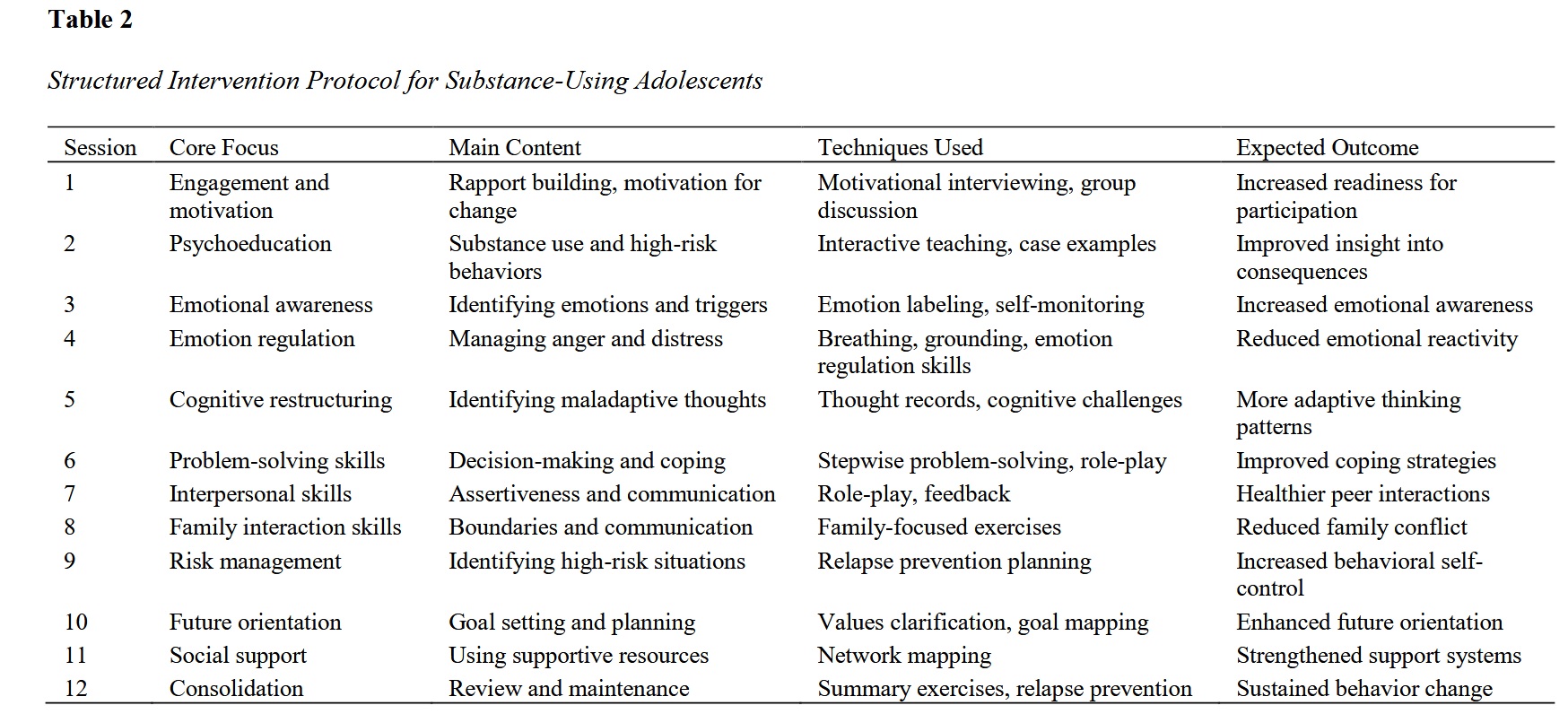
Methods and Materials: This study employed a mixed-methods sequential exploratory design. In the qualitative phase, semi-structured interviews were conducted with substance-using adolescents, clinicians, and experts to identify core psychological, familial, and social mechanisms underlying high-risk behaviors, and the findings were used to develop a structured intervention protocol. In the quantitative phase, a quasi-experimental pretest–posttest design with an intervention and a control group was implemented. Participants were adolescents with a history of substance use recruited from counseling and support centers in Shahroud. The intervention group received a structured, multi-session program focusing on emotion regulation, cognitive restructuring, problem-solving, interpersonal skills, and future orientation, while the control group received routine services. Standardized self-report measures of high-risk behaviors were administered before and after the intervention.
Findings: Inferential analyses revealed a statistically significant reduction in high-risk behaviors in the intervention group compared to the control group. Repeated-measures analysis showed a significant time × group interaction, indicating that changes over time differed significantly between groups. The intervention produced large effect sizes for overall high-risk behaviors as well as for emotional, behavioral, and social risk components, demonstrating the strong impact of the structured program beyond natural change or routine care.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that a structured intervention developed through qualitative exploration and evaluated using quantitative methods can effectively reduce high-risk behaviors among substance-using adolescents. Integrating emotional, cognitive, and interpersonal components within a coherent framework appears to be a promising approach for intervention programs targeting adolescent substance use.
Downloads
References
Avcı, M. (2025). Adolescents' experiences with substance use: risks, protective factors and interventions. BMC psychology, 13(1), 802. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-025-03125-w
Botvin, G. J., & Griffin, K. W. (2007). School-based programs to prevent substance use. Journal of Primary Prevention, 28(3-4), 213-232. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18092239/
Compas, B. E., Jaser, S. S., & Dunbar, J. P. (2014). Coping and emotion regulation in adolescence. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 24(2), 362-379. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28616996/
Dishion, T. J., & Tipsord, J. M. (2021). Peer contagion in adolescent substance use. Child Development Perspectives, 5(2), 131-136. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19575606/
Eisenberg, N., Spinrad, T. L., & Eggum, N. (2015). Emotion-related self-regulation in childhood and adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 22(1), 17-38. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3018741/
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Miller, J. Y. (2019). Risk and protective factors for adolescent substance use. Psychological bulletin, 112(1), 64-105. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.64
Kobulsky, J., Schroeder, K., Schuler, B., Patrick, E., Lang, Y., & Wu, J. (2024). Developmental timing of child maltreatment in relation to obesity and substance use disorder in late adolescence. Psychology of violence, 14(1), 24-33. https://doi.org/10.1037/vio0000495
Komissarova, O. A., & Милованова, О. А. (2024). Subjective Experience of Loneliness as a Predictor of Substance Use in Adolescents. Психолог(6), 161-173. https://doi.org/10.25136/2409-8701.2024.6.72573
Kumpfer, K. L., & Alvarado, R. (2003). Family-strengthening approaches for substance abuse prevention. American psychologist, 58(6-7), 457-465. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.58.6-7.457
López-Martínez, L. F., Carretero, E. M., Carrasco, M. A., & Pérez-García, A. M. (2025). Self-Regulation, Emotional Symptomatology, Substance Use, and Social Network Addiction in Adolescent Self-Harm. Behavioral Sciences, 15(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15030257
Merrin, G. J., Bailey, J. A., Kelly, A. B., Le, V. T., Heerde, J. A., Doery, E., Batmaz, E. A., & Toumbourou, J. W. (2024). Continuity and Change in Substance Use Patterns During the Transition From Adolescence to Young Adulthood: Examining Changes in Social Roles. International journal of mental health and addiction, 23(6), 4155-4177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-024-01342-9
Montero‐Zamora, P., López-Soto, A., Cordoba, J., & Ramirez, E. (2025). Adolescent Substance Use in Costa Rica: Findings From a National Survey Among Secondary School Students. Frontiers in Public Health, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1655355
Mousavi, S., & Fallahi, M. (2020). The role of family in preventing risky behaviors in adolescents. Quarterly Journal of Family Studies, 16(1), 91-108. https://en.civilica.com/doc/2340032/
Olave, L., Momeñe, J., Macía, L., Macía, P., María Dolores del Rocío Chávez, V., Herrero, M., Estévez, A., & Díez, I. I. (2024). Substance Use and Its Relationship With Attachment and Early Maladaptive Schemes in Adolescents in Ecuador. Developmental Psychobiology, 66(6). https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.22532
Parveen, A., & Jan, S. (2024). Parent-child conflict: A risk factor for substance abuse among adolescents. Education Mind, 3(1), 19-30. https://doi.org/10.58583/Pedapub.EM2403
Rajamani, J. B., Reshmi, Y. S., Pricilla, R. A., Prasad, J., & Baskar, M. (2024). Prevalence of Substance Use Among Adolescents Residing in Urban Slums of Vellore: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 13(11), 4831-4836. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_420_24
Rogers, A. H., Palermo, T. M., Groenewald, C. B., & Murray, C. B. (2024). Adolescent Predictors of Substance Use in Young Adulthood Among Individuals With Childhood‐onset Chronic Pain: A follow‐up Study. European Journal of Pain, 29(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.4724
Shoshani, A. (2024). Risk and Protective Factors for Substance Use and Media Addictive Behaviors in Adolescents During the COVID‐19 Pandemic. Journal of adolescence, 96(4), 746-759. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12295
Singh, D., Azuan, M. A., & Narayanan, S. (2024). High-risk sexual behavior among Malaysian adolescents who use drugs: a mixed-methods study of a sample in rehabilitation. Journal of Substance Use, 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659891.2024.2329885
Singh, D., Schumacher, H., Pellegrino, C. A., Holmes, B., Garfield, R. L., & Harder, V. S. (2024). Assessing Strengths and Well-Being in Primary Care for Adolescents With Mental Health and Substance Use Concerns. Clinical Pediatrics, 64(3), 340-347. https://doi.org/10.1177/00099228241264769
Steinberg, L. (2014). Age of opportunity: Lessons from the new science of adolescence. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=sppdBAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Steinberg,+L.+(2014).+Age+of+opportunity:+Lessons+from+the+new+science+of+adolescence,+Boston:+Houghton+Mifflin+Harcourt.+%09&ots=Adta39l2CR&sig=GKzO3qOxkH-FAOz7gfHpgQNjCbI
Swaim, R. C., Crabtree, M. A., & Egli, M. (2025). A Structural Equation Model Test of Affect, Family Warmth, and Substance Use Among American Indian Reservation-Based Adolescents. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 39(4), 345-353. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0001068
Tangney, J. P., Baumeister, R. F., & Boone, A. L. (2004). High self-control predicts good adjustment. Journal of personality, 72(2), 271-324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3506.2004.00263.x
Wills, T. A., & Dishion, T. J. (2024). Temperament and adolescent substance use. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33(1), 69-81. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_7