Explainable AI Forecast of Psychological Distress in Adolescents Based on Family Conflict, School Pressure, and Emotion Regulation Capacity
Keywords:
Adolescent mental health, psychological distress, explainable artificial intelligence, emotion regulation, family conflict, school pressureAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to develop and interpret an explainable artificial intelligence model for forecasting psychological distress in adolescents by quantifying the joint and individual contributions of family conflict, school pressure, and emotion regulation capacity.
Methods and Materials: This cross-sectional study was conducted among 1,142 secondary school students aged 13–18 years in Germany using multi-stage cluster sampling. Participants completed validated self-report measures of psychological distress, family conflict, school pressure, and emotion regulation capacity. Data were analyzed using an explainable gradient boosting machine learning framework with five-fold cross-validation. Model performance was evaluated using root mean square error, mean absolute error, and coefficient of determination. Feature contributions and interaction effects were examined using Shapley Additive Explanations and partial dependence analyses to ensure full interpretability of predictions.
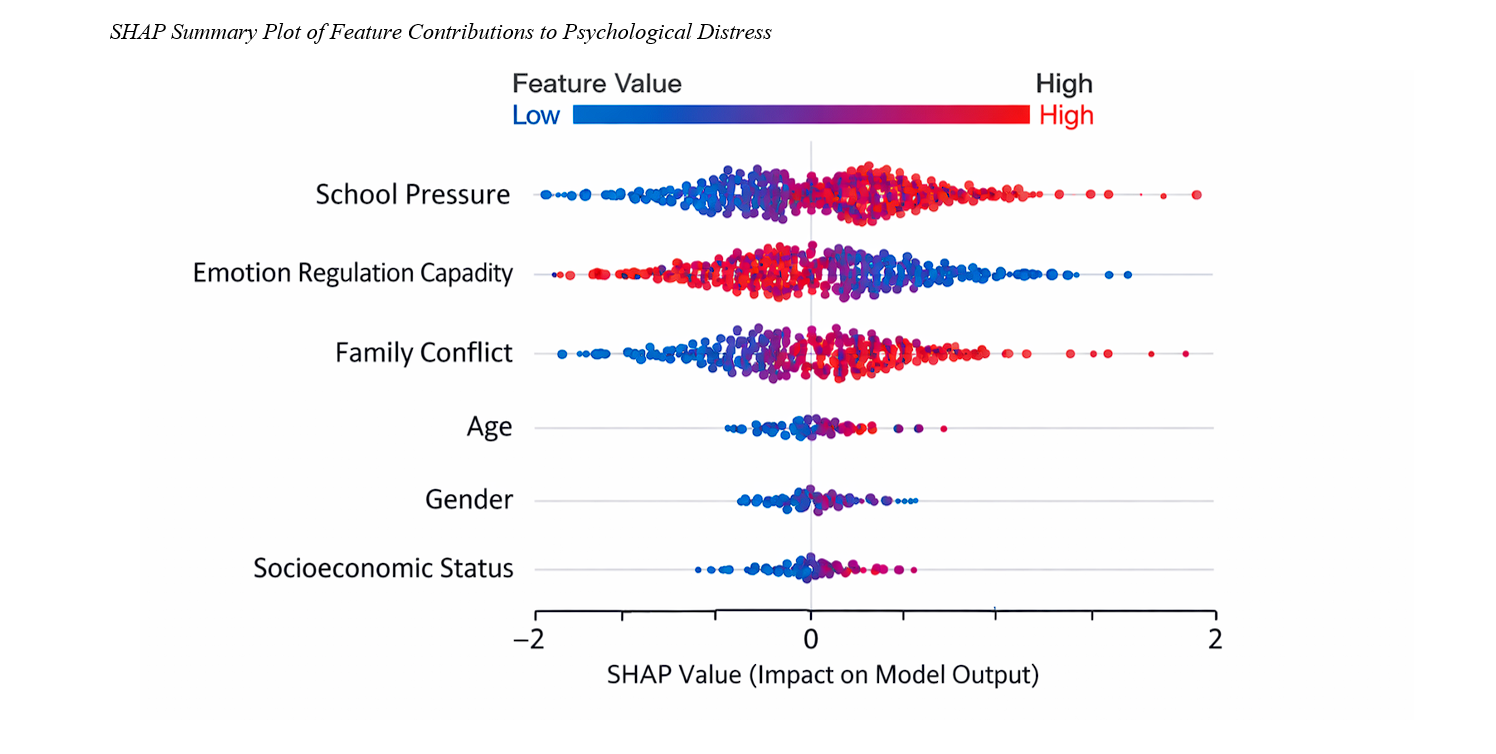
Findings: The explainable model demonstrated strong predictive accuracy, accounting for 69% of the variance in adolescent psychological distress on the test dataset (R² = 0.69, RMSE = 3.58, MAE = 2.71). Feature attribution analysis revealed that school pressure was the most influential predictor (36.2% relative contribution), followed by emotion regulation capacity (31.1%) and family conflict (24.7%), while demographic variables showed minimal impact. Interaction analyses indicated that high emotion regulation capacity substantially attenuated the negative effects of elevated school pressure and family conflict on psychological distress.
Conclusion: Adolescent psychological distress is primarily shaped by the combined influence of academic stress, family dynamics, and emotional self-regulation. Explainable artificial intelligence provides a powerful and transparent framework for identifying individualized risk profiles and informing targeted mental health interventions in educational and clinical settings.
Downloads
References
Brites, R., Brandão, T., Hipólito, J., Jiménez-Ros, A. M., & Nunes, O. (2023). Emotion Regulation, Resilience, and Mental Health: A Mediation Study With University Students in the Pandemic Context. Psychology in the Schools, 61(1), 304-328. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.23055
Carroll, R. C., Murphy, J., & Myers, J. S. (2024). Mindful Transformation: Investigating the Effects of a 10-Week Graduate-Level Mindfulness Course Among Nursing Students Through a Mixed Methods Approach. Journal of Holistic Nursing, 42(4), 393-408. https://doi.org/10.1177/08980101241249792
Fujita, J., Aoyama, K., Saigusa, Y., Miyazaki, H., Aoki, Y., Asanuma, K., Takahashi, Y., & Hishimoto, A. (2022). Problematic Internet Use and Daily Difficulties Among Adolescents With School Refusal Behaviors. Medicine, 101(7), e28916. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000028916
Gautam, N., Rahman, M. M., Hashmi, R., Lim, A., & Khanam, R. (2024). Socioeconomic Inequalities in Child and Adolescent Mental Health in Australia: The Role of Parenting Style and Parents’ Relationships. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-024-00719-x
Giridharan, S., & Pandiyan, B. (2024). A Path to Resilience: The Impact of School-Based Yoga on Adolescent Mental Well-Being. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.73604
Hawes, M. T., Szenczy, A. K., Klein, D. N., Hajcak, G., & Nelson, B. D. (2021). Increases in Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Adolescents and Young Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Psychological medicine, 52(14), 3222-3230. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291720005358
Hu, S., Li, X., & Yang, L. (2023). Effects of Physical Activity in Child and Adolescent Depression and Anxiety: Role of Inflammatory Cytokines and Stress-Related Peptide Hormones. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1234409
Källmén, H., & Hallgren, M. (2021). Bullying at School and Mental Health Problems Among Adolescents: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-021-00425-y
Karam, J.-M., Fekih‐Romdhane, F., Fawaz, M., Malaeb, D., Obeïd, S., & Hallit, S. (2023). The Moderating Effect of Emotion Regulation in the Association Between Social Support and Religiosity and Psychological Distress in Adults. BMC psychology, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01160-z
Keleynikov, M., Cohen, N., & Benatov, J. (2024). Maternal Distress During the COVID-19 Outbreak: A Socio-Ecological Perspective. PLoS One, 19(5), e0302266. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0302266
Khunti, K., Boniface, S., Norris, E., Oliveira, C. d., & Shelton, N. (2022). The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health in School-Aged Children: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of Randomised Control Trials. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 28(3), 1217-1238. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591045221136016
LaMontagne, L., Diehl, D. C., Doty, J., & Smith, S. (2022). The Mediation of Family Context and Youth Depressive Symptoms by Adolescent Emotion Regulation. Youth & Society, 55(3), 552-580. https://doi.org/10.1177/0044118x211067266
Lanjekar, P. D., Joshi, S. H., Lanjekar, P. D., & Wagh, V. (2022). The Effect of Parenting and the Parent-Child Relationship on a Child's Cognitive Development: A Literature Review. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.30574
Li, Z., Li, J., Kong, J., Li, Z., Wang, R., & Jiang, F. (2024). Adolescent Mental Health Interventions: A Narrative Review of the Positive Effects of Physical Activity and Implementation Strategies. Frontiers in psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1433698
Martínez-Lorca, M., Zabala-Baños, M. C., Calvo, S. M., Romo, R. A., & Lorca, A. M. (2022). Assessing Emotional, Empathic and Coping Skills in Spanish Undergraduates in Health Sciences and Social Sciences. Retos, 47, 126-137. https://doi.org/10.47197/retos.v47.94344
McFayden, T. C., Breaux, R., Bertollo, J. R., Cummings, K., & Ollendick, T. H. (2021). COVID-19 Remote Learning Experiences of Youth With Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Rural Appalachia. Rural Mental Health, 45(2), 72-85. https://doi.org/10.1037/rmh0000171
Pu, D. F., & Rodriguez, C. M. (2023). Child and Parent Factors Predictive of Mothers’ and Fathers’ Perceived Family Functioning. Journal of Family Psychology, 37(1), 121-131. https://doi.org/10.1037/fam0000971
Ratnam, K. K. Y., Farid, N. D. N., Yakub, N. A., & Dahlui, M. (2022). The Effectiveness of the Super Skills for Life (SSL) Programme in Promoting Mental Wellbeing Among Institutionalised Adolescents in Malaysia: An Interventional Study. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(15), 9324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159324
Renati, R., Bonfiglio, N. S., & Rollo, D. (2023). Italian University Students’ Resilience During the COVID-19 Lockdown—A Structural Equation Model About the Relationship Between Resilience, Emotion Regulation and Well-Being. European Journal of Investigation in Health Psychology and Education, 13(2), 259-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13020020
Rohrig, S., Bennett, S. M., Desai, P., Zendegui, E., & Chiu, A. W. (2023). A Description of School Refusal Behavior in Adolescents Prior to Acute Care Admission. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 32(4), 226-238. https://doi.org/10.1177/10634266231187369
Russell, B. S., Hutchison, M., Tambling, R. R., Tomkunas, A. J., & Horton, A. L. (2020). Initial Challenges of Caregiving During COVID-19: Caregiver Burden, Mental Health, and the Parent–Child Relationship. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 51(5), 671-682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-020-01037-x
Silk, J. S., Scott, L. N., Hutchinson, E., Lu, C., Sequeira, S., McKone, K. M., Quyen, B., & Ladouceur, C. D. (2021). Storm Clouds and Silver Linings: Day-to-Day Life in COVID-19 Lockdown and Emotional Health in Adolescent Girls. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 47(1), 37-48. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsab107
Spinelli, M., Lionetti, F., Pastore, M., & Fasolo, M. (2020). Parents' Stress and Children's Psychological Problems in Families Facing the COVID-19 Outbreak in Italy. Frontiers in psychology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01713
Steffie van der Mey‐, B., Vuijk, P., Bul, K., Lier, P. A. C. v., Sijbrandij, M., Maras, A., & Buil, J. M. (2025). Co‐Rumination as a Moderator Between Best‐Friend Support and Adolescent Psychological Distress. Journal of adolescence, 97(5), 1161-1172. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12483
Stone, L. B., Silk, J. S., Lewis, G., Banta, M. C., & Bylsma, L. M. (2022). Adolescent Girls’ Intrapersonal and Interpersonal Parasympathetic Regulation During Peer Support Is Moderated by Trait and State Co‐rumination. Developmental Psychobiology, 64(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.22232
Tanguy, W. J., Kaur, K., & Asnaani, A. (2024). Using a Transdiagnostic Approach to Examine the Associations Among Internalizing Symptoms, Emotion Regulation, and Distress Tolerance. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology, 15(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/20438087241249682
Teuber, M., Leyhr, D., & Sudeck, G. (2024). Physical Activity Improves Stress Load, Recovery, and Academic Performance-Related Parameters Among University Students: A Longitudinal Study on Daily Level. BMC public health, 24(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18082-z
Torales, J., Torres-Romero, A. D., Barrios, I., O’Higgins, M., Caycho‐Rodríguez, T., Castaldelli-Maia, J. M., & Ventriglio, A. (2025). Mental Health, Emotional Regulation, and Psychosocial Work Factors Among Scientific Researchers: A Cross-Sectional Study From Paraguay. Brain Sciences, 15(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15010065
Uzun, B., Orman, A., & Essau, C. A. (2024). Integrating “Super Skills for Exams” Programme in the School Curriculum to Support Adolescents Preparing for Their National Examinations in Turkey. Children, 11(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11020180
Vacca, M., Cerolini, S., Zegretti, A., Zagaria, A., & Lombardo, C. (2023). Bullying Victimization and Adolescent Depression, Anxiety and Stress: The Mediation of Cognitive Emotion Regulation. Children, 10(12), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121897
Vincenzo, C. D., Pontillo, M., Bellantoni, D., Luzio, M. D., Lala, M. R., Villa, M., Demaria, F., & Vicari, S. (2024). School Refusal Behavior in Children and Adolescents: A Five-Year Narrative Review of Clinical Significance and Psychopathological Profiles. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 50(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-024-01667-0
Yani, D. I., Chua, J. Y. X., Wong, J. C. M., Pikkarainen, M., Goh, Y. S., & Shorey, S. (2025). Perceptions of Mental Health Challenges and Needs of Indonesian Adolescents: A Descriptive Qualitative Study. International journal of mental health nursing, 34(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/inm.13505
Ye, B., Zhao, S., Zeng, Y., Chen, C., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Perceived Parental Support and College Students’ Depressive Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Roles of Emotion Regulation Strategies and Resilience. Current Psychology, 42(23), 20275-20286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03049-3
Zapata, S. M., & Onwuegbuzie, A. J. (2022). Emotion Differentiation and Negative Emotional States: The Mediating Role of Perceived Academic Control and the Moderated Effect of Intrinsic Motivation. Current Psychology, 42(30), 26033-26049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03697-5