Interpretable Gradient Boosting Analysis of Academic Cheating in Adolescents Using Moral Disengagement and Achievement Goals
Keywords:
Academic cheating, moral disengagement, achievement goal orientations, adolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to develop an interpretable machine learning model to examine the predictive roles of moral disengagement and achievement goal orientations in academic cheating among high school adolescents.
Methods and Materials: The study employed a cross-sectional correlational design with a predictive analytics framework and was conducted among 681 adolescents aged 14–18 years enrolled in public high schools in California. Participants completed standardized self-report measures assessing academic cheating behavior, moral disengagement, and achievement goal orientations, along with demographic information. Data were analyzed using an Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) regression model with five-fold cross-validation and Bayesian hyperparameter optimization. Model performance was evaluated using root mean squared error, mean absolute error, and explained variance. To ensure interpretability, Shapley Additive Explanations were applied to quantify the relative and local contributions of predictors, and partial dependence analyses were conducted to examine nonlinear and interactive effects.
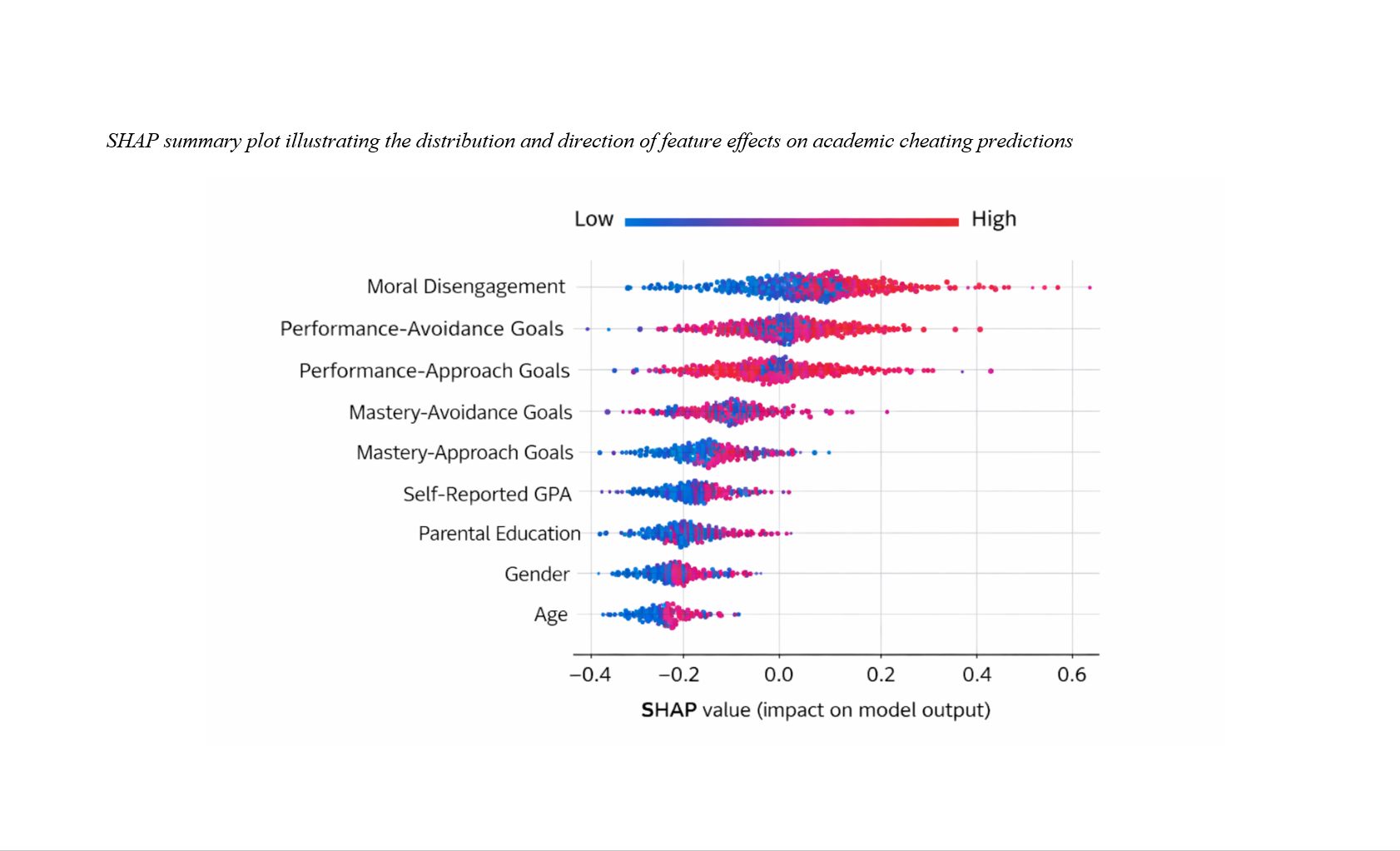
Findings: The gradient boosting model demonstrated strong predictive performance, accounting for 56% of the variance in academic cheating. Moral disengagement emerged as the most influential predictor, followed by performance-avoidance and performance-approach goals. Mastery-approach goals exhibited a consistent negative association with cheating. The model identified nonlinear threshold effects for moral disengagement and significant interaction patterns between motivational orientations and moral cognition, indicating that performance-based goals amplified the impact of moral disengagement on cheating behavior.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that academic cheating in adolescence is primarily driven by cognitive moral mechanisms operating in conjunction with achievement-related motivational pressures. Interpretable machine learning offers a powerful framework for uncovering these complex psychological dynamics and provides actionable insights for the design of targeted educational interventions aimed at promoting academic integrity.
Downloads
References
Boardley, I. D., Zhang, S., Gunning, S. A., & Adie, J. W. (2025). Latent Motivation Profiles and Doping in Sport and Exercise: An Integrative Approach Based on Achievement Goal and Self‐Determination Theories. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 35(9). https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.70138
Burns, P., Teng, F., Omondi, A. A., Burton, E. T., & Ward, L. M. (2022). Sex Education and Sexual Risk Behavior Among Adolescents and Youth in the Deep South: Implications for Youth HIV Prevention. Southern Medical Journal, 115(5), 310-314. https://doi.org/10.14423/smj.0000000000001391
Dias-Oliveira, E., Morais, C., & Pasion, R. (2022). Psychopathic Traits, Academic Fraud, and the Mediating Role of Motivation, Opportunity, Rationalization and Perceived Capability. Journal of Individual Differences, 43(1), 10-19. https://doi.org/10.1027/1614-0001/a000349
Doron, J., Hayotte, M., d’Arripe-Longueville, F., & Leprince, C. (2023). Coping Profiles of Adolescent Football Players and Association With Interpersonal Coping: Do Emotional Competence and Psychological Need Satisfaction Matter? Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 34(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.14550
H, M. R., Cui, Y. X., Hill, N. E., Liang, B., & Perella, J. (2025). Adolescent Self‐efficacy and Orientation About the Future: Longitudinal Associations With Family/School Support and Sense of Purpose. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 35(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.70055
He, Q., Yang, Z., Yu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2023). The Dark Triad, Performance Avoidance, and Academic Cheating. PsyCh Journal, 12(3), 461-463. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.632
Hill, P. L., & Burrow, A. L. (2021). Why Youth Are More Purposeful Than We Think. Child Development Perspectives, 15(4), 281-286. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12432
Kamran, K., Azam, A., & Atif, M. M. (2022). Supervisor Bottom-Line Mentality, Performance Pressure, and Workplace Cheating: Moderating Role of Negative Reciprocity. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.801283
Karam, A., Thompson, P., & Waltzer, T. (2025). Effects of Perceived Achievement on Academic Integrity Behaviors in Students From High School X. Journal of Student Research, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.47611/jsrhs.v14i1.8864
Kazem, K. S. (2024). Academic Honesty and Its Relationship to Moral Development Among University Students. International Journal of Religion, 5(7), 996-1010. https://doi.org/10.61707/pvxt3v27
Khan, A. G., Mahmood, M., Islam, M. S., Li, Y., & Hwang, H. J. (2023). Why and When Does Performance Pressure Encourage Employee Expediency? A Moderated Mediation Model. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 73(7), 2235-2253. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijppm-01-2023-0037
Li, Q. (2025). Meta-Analysis on the Relationship Between Achievement Goal Orientation and Cheating Behavior. Inst Educ Res Gyeongin Natl Univ Educ, 45(1), 173-196. https://doi.org/10.25020/je.2025.45.1.173
Liu, Z., Zhang, X., Xu, H., Deng, H., Li, J., & Lan, Y. (2022). The Effect of I-Deals on Employees’ Unethical Behavior During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Roles of Hubristic Pride and Grandiose Narcissism. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.938864
Monge, C. K., & Matthews, N. L. (2024). Blaming the Smurf: Using a Novel Social Deception Behavior in Online Games to Test Attribution Theories. New Media & Society, 27(7), 4181-4204. https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448241235638
Moura, H. M. d., Gouveia, R. S. V., Alex Sandro de Moura, G., Figueiredo, C. V. d., & Gouveia, V. V. (2022). Cheating Motivation Scale: Evidence of Validity and Reliability. Psico-USF, 27(3), 425-436. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-82712023270302
Niayatulloh, A., & Haikal, M. (2024). Identification of Cheating Methods in Large-Scale Tests: Islamic Education Subject Matter in the National Examination. Educenter Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan, 3(1), 10-26. https://doi.org/10.55904/educenter.v3i1.1103
Pérez, M. R. (2022). The Relationship Between Academic Psychological Capital and Academic Coping Stress Among University Students. Terapia psicológica, 40(2), 279-305. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-48082022000200279
Příhodová, T., Preiss, M., Heissler, R., Straková, E., Sanders, E., & Harsa, P. (2021). The Relationship Between Work Integrity and Other Variables and Behaviors. Studia psychologica, 63(1), 24-42. https://doi.org/10.31577/sp.2021.01.812
Saladino, V., Mosca, O., Lauriola, M., Hoelzlhammer, L., Cabras, C., & Verrastro, V. (2020). Is Family Structure Associated With Deviance Propensity During Adolescence? The Role of Family Climate and Anger Dysregulation. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(24), 9257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249257
Shi, Y., Mao, J. Y., & Xu, J. (2025). Blessing or Curse? When and Why Stretch Goal Promotes and Inhibits Employee Job Progression. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 98(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/joop.70019
Tahrir, T., Nurdin, F. S., & Damayanti, I. R. (2020). The Role of Critical Thinking as a Mediator Variable in the Effect of Internal Locus of Control on Moral Disengagement. International Journal of Instruction, 13(1), 17-34. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2020.1312a
Thiel, C. E., Bonner, J., Bush, J., Welsh, D., & Garud, N. (2021). Stripped of Agency: The Paradoxical Effect of Employee Monitoring on Deviance. Journal of Management, 49(2), 709-740. https://doi.org/10.1177/01492063211053224
Ulmanen, S., Soini, T., Pietarinen, J., & Pyhältö, K. (2022). Development of Students’ Social Support Profiles and Their Association With Students’ Study Wellbeing. Developmental Psychology, 58(12), 2336-2349. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001439
Wang, P. C., & Read, S. J. (2024). Pavlovian Cues Boost Self-Regulation: Predicting Success With Conditioned Stimuli. Motivation Science, 10(4), 299-312. https://doi.org/10.1037/mot0000356
Watts, F. M., Dood, A. J., Shultz, G. V., & Rodriguez, J.-M. G. (2023). Comparing Student and Generative Artificial Intelligence Chatbot Responses to Organic Chemistry Writing-to-Learn Assignments. Journal of Chemical Education, 100(10), 3806-3817. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00664
Welsh, D., Baer, M. D., Sessions, H., & Garud, N. (2020). Motivated to Disengage: The Ethical Consequences of Goal Commitment and Moral Disengagement in Goal Setting. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 41(7), 663-677. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2467
Yau, P. S., Cho, Y. W., Kay, J., & Heckhausen, J. (2022). The Effect of Motive-Goal Congruence on Adolescents’ Academic Goal Engagement and Disengagement. Motivation and Emotion, 46(4), 447-460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-022-09946-1
Yau, P. S., Cho, Y. W., Shane, J., Kay, J., & Heckhausen, J. (2021). Parenting and Adolescents’ Academic Achievement: The Mediating Role of Goal Engagement and Disengagement. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 31(4), 897-909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-021-02007-0
Zhang, Y., He, B., Huang, Q., & Xie, J. (2020). Effects of Supervisor Bottom-Line Mentality on Subordinate Unethical Pro-Organizational Behavior. Journal of managerial psychology, 35(5), 419-434. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmp-11-2018-0492