Exploring the Components of Psychological Inflexibility in Youth with Perfectionist Traits
Keywords:
Perfectionism, Psychological inflexibility, Youth, Cognitive rigidity, Emotional avoidance, Interpersonal strainAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the key components of psychological inflexibility in youth with perfectionist traits, focusing on how cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and interpersonal processes contribute to maladaptive outcomes.
Methods and Materials: A qualitative research design was employed using semi-structured interviews with 26 participants aged 18–25 from Mexico who self-identified as having perfectionist tendencies. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling, ensuring diversity in gender, education, and socioeconomic background. Data collection continued until theoretical saturation was achieved. All interviews were transcribed verbatim and analyzed thematically using NVivo 14 software. To ensure rigor, constant comparison, peer debriefing, and iterative coding were conducted, leading to the identification of central themes and subthemes.
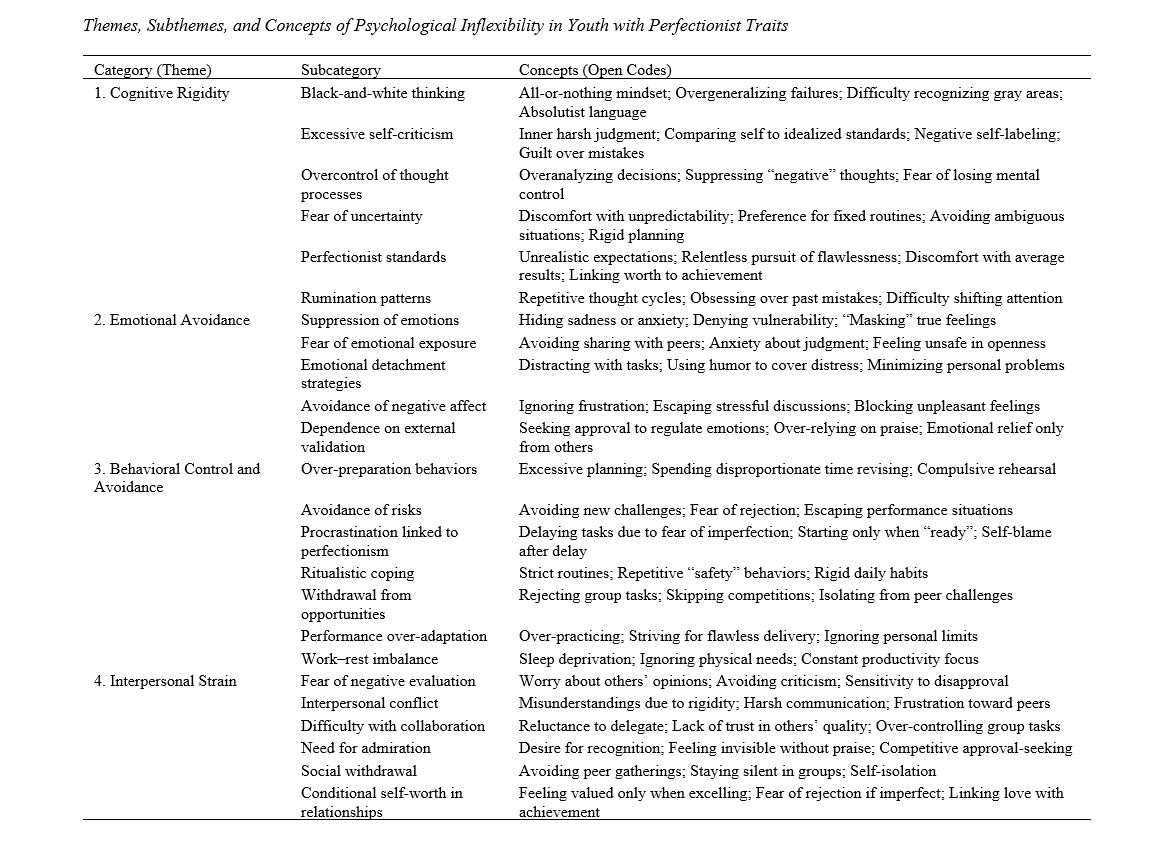
Findings: Analysis revealed four overarching themes of psychological inflexibility in perfectionist youth: (1) cognitive rigidity, including black-and-white thinking, failure sensitivity, and rumination; (2) emotional avoidance, characterized by suppression of emotions, reliance on external validation, and detachment strategies; (3) behavioral control and avoidance, manifested in over-preparation, procrastination, rigid routines, and withdrawal from opportunities; and (4) interpersonal strain, encompassing fear of negative evaluation, conditional self-worth, and difficulties with collaboration. These findings indicate that perfectionist youth experience a reinforcing cycle where rigid standards amplify inflexibility, sustaining maladaptive coping and social disconnection.
Conclusion: The study demonstrates that psychological inflexibility is a central mechanism through which perfectionism leads to maladaptive outcomes in youth. By illuminating the lived experiences of young perfectionists, this research provides insights into how cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and interpersonal patterns interact to maintain inflexibility. The findings underscore the need for interventions, such as Acceptance and Commitment Therapy, that cultivate psychological flexibility and support adaptive coping in perfectionist youth.
Downloads
References
Aleeza, A., & Bintari, D. R. (2023). Trait Anxiety and Eating Disorder Symptoms: Psychological Inflexibility as Mediator. Insan Jurnal Psikologi Dan Kesehatan Mental, 8(2), 117-147. https://doi.org/10.20473/jpkm.v8i22023.117-147
Andrade, G., Gaudreau, P., & Pétrin‐Pomerleau, P. (2024). The Basic Psychological Needs in Excellencism and Perfectionism: A Dual Perspective With the Need-as-Motives and the Need-as-Nutriments Frameworks. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/thvug
Balboula, M. Z., & Elfar, E. E. (2024). Do Perfectionism Types Matter? Auditors' Ability to Detect Fraud and the Moderating Role of Time Budget Pressure: Evidence From Egypt. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting. https://doi.org/10.1108/jfra-11-2023-0657
Barrado‐Moreno, V., Esteve, R., McCracken, L. M., & Ramírez‐Maestre, C. (2025). The Mediating Role of Psychological Flexibility and Inflexibility Between Impulsivity and Opioid Misuse in People With Chronic Noncancer Pain. European Journal of Pain, 29(6). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.70048
Callahan, K. E., Stori, S. A., & Donahue, J. J. (2020). Psychological Inflexibility Processes and Nonsuicidal Self‐injury: Concurrent and Prospective Associations. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 77(6), 1394-1411. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.23086
Chen, L., Chen, G.-H., Wang, S., & Jiang, L. (2023). The Effect of Perfectionism on Consumers’ Intentions to Purchase Imperfect Products. Behavioral Sciences, 13(3), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13030269
Clarke, P., Sheffield, D., & Akehurst, S. (2020). Personality Predictors of Yips and Choking Susceptibility. Frontiers in psychology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02784
Dang, S. S., Quesnel, D. A., Hewitt, P. L., Flett, G. L., & Deng, X. (2020). Perfectionistic Traits and Self‐presentation Are Associated With Negative Attitudes and Concerns About Seeking Professional Psychological Help. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 27(5), 621-629. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.2450
Doktorová, D., & Piteková, N. (2020). Tripartite Typology of Perfectionism Among Psychology Students. Postmodern Openings, 11(1Sup1), 45-60. https://doi.org/10.18662/po/11.1sup1/122
Flett, G. L., & Hewitt, P. L. (2022). Keys to Understanding Perfectionistic Children. 79-95. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000289-006
García‐Rubio, C., Lecuona, Ó., Blanco‐Donoso, L. M., Cantero-García, M., Paniagua, D., & Rodríguez‐Carvajal, R. (2020). Spanish Validation of the Short-Form of the Avoidance and Fusion Questionnaire (AFQ-Y8) With Children and Adolescents. Psychological assessment, 32(4), e15-e27. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000801
Jang, S. J., Kim, E., & Lee, H. (2023). Effects of Personality Traits and Mentalization on Workplace Bullying Experiences Among Intensive Care Unit Nurses. Journal of nursing management, 2023, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/5360734
Kummer, K., Mattes, A., & Stähl, J. (2023). Do Perfectionists Show Negative, Repetitive Thoughts Facing Uncertain Situations? Current Psychology, 43(3), 2387-2402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04409-3
Kuru, T., & Şahin, C. (2023). The Effect of Psychological Inflexibility on Health-Related Quality of Life, Depression, and Anxiety in Patients With Chronic Tinnitus Without Hearing Loss. Revista Da Associação Médica Brasileira, 69(4). https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.20221142
Law, N. K. (2023). The Impact of Exam Stress on the Relationship Between Autistic Traits and Disordered-Eating Attitudes in a Non-Clinical Population. Reinvention an International Journal of Undergraduate Research, 16(2). https://doi.org/10.31273/reinvention.v16i2.783
Li, D., Cui, Y., Liu, Y., Zheng, Y., Zeng, Y., & Cheng, A. S. K. (2021). A Chain Mediation Model of Perceived Stress, Neuroticism, and Psychological Inflexibility on Depressive Symptoms of Chinese New Fathers. American Journal of Men S Health, 15(5). https://doi.org/10.1177/15579883211054351
Lipsker, C. W., Hirvikoski, T., Balter, L. J. T., Bölte, S., Lekander, M., Holmström, L., & Wicksell, R. K. (2021). Autistic Traits and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms Associated With Greater Pain Interference and Depression, and Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life in Children With Chronic Pain. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.716887
Liu, Q., Zhao, X., & Liu, W. (2022). Are Perfectionists Always Dissatisfied With Life? An Empirical Study From the Perspective of Self-Determination Theory and Perceived Control. Behavioral Sciences, 12(11), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12110440
Malik, M. F. (2023). “Perfectionism Is a Debacle” How a perfectionist Leader Hinders in Business Processes? A Multiple Mediated Model. Business Process Management Journal, 29(4), 1184-1203. https://doi.org/10.1108/bpmj-10-2022-0534
Sudhakar, S., Jose, J. P., & Cherayi, S. (2021). A Cross Sectional Survey of Factors Influencing Healthcare Access in Older Women of South India. Innovation in Aging, 5(Supplement_1), 829-830. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igab046.3041
White, R. G., Larkin, P., McCluskey, J., Lloyd, J., & McLeod, H. J. (2020). The Development of the ‘Forms of Responding to Self-Critical Thoughts Scale’ (FoReST). Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 15, 20-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2019.11.003
Yosopov, L., Saklofske, D. H., Smith, M. M., Flett, G. L., & Hewitt, P. L. (2024). Failure Sensitivity in Perfectionism and Procrastination: Fear of Failure and Overgeneralization of Failure as Mediators of Traits and Cognitions. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 42(6), 705-724. https://doi.org/10.1177/07342829241249784
Березовский, А. В., Улюкин, И. М., & Орлова, Е. С. (2020). Рerfectionism of Young People. Bulletin of the Russian Military Medical Academy, 22(2), 195-198. https://doi.org/10.17816/brmma50072
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








