Explainable AI Analysis of Grit, Academic Hope, and Persistence in Iranian EFL Students
Keywords:
Explainable artificial intelligence; grit; academic hope; academic persistence; EFL learners; motivational psychologyAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to examine the predictive roles and relative importance of grit and academic hope in explaining academic persistence among Iranian EFL students using explainable artificial intelligence techniques.
Methods and Materials: This study employed a cross-sectional correlational design with a sample of Iranian EFL learners enrolled in language institutes and university language centers in Tehran. Participants completed standardized self-report measures assessing grit (perseverance of effort and consistency of interests), academic hope (agency and pathways), and academic persistence. Data were analyzed using supervised machine learning models suitable for psychological tabular data, with academic persistence specified as the outcome variable and grit and academic hope components as predictors. Model performance was evaluated using explained variance and error-based indices. To ensure interpretability, explainable AI methods, specifically SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), were applied to identify global and local feature contributions and to clarify the direction and magnitude of predictor effects.
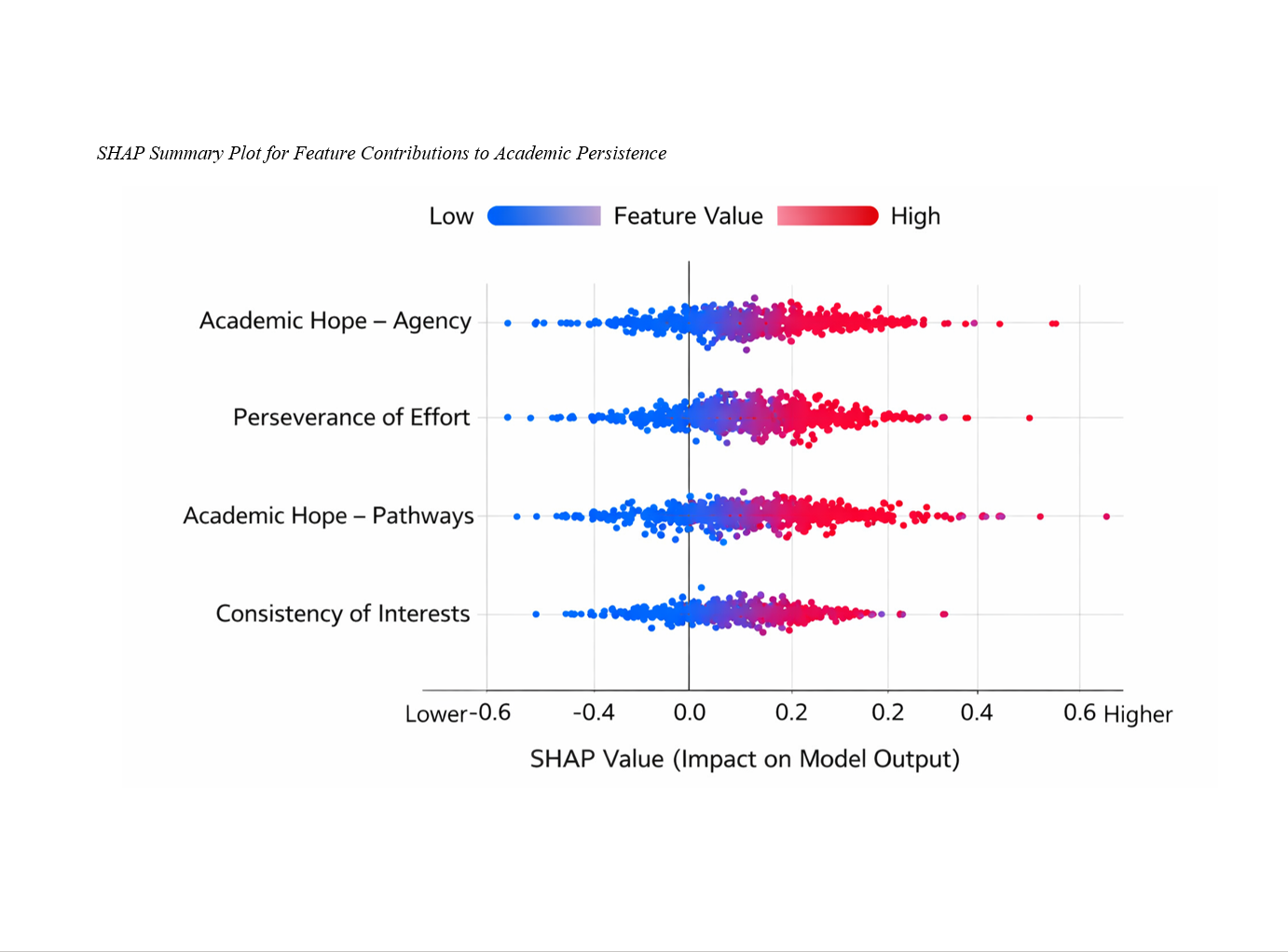
Findings: The machine learning model explained a substantial proportion of variance in academic persistence, indicating strong predictive performance. Explainable AI analyses revealed that academic hope–agency was the most influential predictor of persistence, followed by perseverance of effort, academic hope–pathways, and consistency of interests. Higher levels of agency beliefs and perseverance of effort were associated with higher predicted persistence scores, while consistency of interests showed a comparatively weaker contribution. The results demonstrated non-linear and differential effects of motivational components on persistence, highlighting individual variability in predictor influence.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that academic persistence among Iranian EFL students is primarily driven by agency-based hope and sustained effort, and that explainable AI provides a powerful framework for uncovering nuanced motivational mechanisms beyond traditional linear models.
Downloads
References
Abri, S., Nouri, M., & Saemi, H. (2025). Investigating the Relationship Between Academic Hope and Academic Vitality with the Academic Achievement of First-grade High School Students in Aliabad Katul County. Journal of Psychological Studies and Educational Sciences, 8(92). https://en.civilica.com/doc/2292972/
Barrientos, P. L. M. (2025). Socio-Emotional Competence and Academic Grit Among Grade Ten Students of the Largest Comprehensive High School. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science, IX(V), 4947-4957. https://doi.org/10.47772/ijriss.2025.905000382
Fowler, R. (2025). The Effect of Grit and Mindset on Professional Pilot Student Persistence Middle Tennessee State University]. https://jewlscholar.mtsu.edu/items/129634df-da2a-4f25-b699-315d19659c55
Groza, I. A., & Tofan, C. M. (2024). Motivational persistence and academic procrastination: The moderating role of behavioural deactivation for Romanian female students. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 22(86), 17–36. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2024-77685-001
Hansen, M. J., Palakal, M., & White, L. J. (2023). The Importance of STEM Sense of Belonging and Academic Hope in Enhancing Persistence for Low-Income, Underrepresented STEM Students. Journal for Stem Education Research, 7(2), 155-180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41979-023-00096-8
He, L., Pan, T., Lu, H., Yu, H., & Cui, J.-H. (2024). The Relationship Between Second Language Grit and Academic Achievement Among Chinese International Students: The Mediating Effect of Learning Engagement. New directions for child and adolescent development, 2024(1). https://doi.org/10.1155/cad/3402460
Henry, A. (2023). Persistence in Language Learning. 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781405198431.wbeal20428
Ibrahim, I. A., Alenezi, A., Hagrass, H. R., & Abdou, H. (2025). Unveiling the Impact of Grit and Learning Agility on Academic Burnout Among Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sage Open Nursing, 11. https://doi.org/10.1177/23779608251346685
kang, m.-g., & Kim, S. (2025). Effects of Adolescent Grit, Parental Supervision, and Academic Stress on Self-Regulated Learning. K Assoc Edu Res, 10(2), 741-754. https://doi.org/10.48033/jss.10.2.36
Lee, M., & Chung, H. (2025). The Structural Relationship Between Adolescents' Relationships With Teachers and Peers and Academic Engagement: Focusing on the Mediating Effects of Self-Esteem and Grit. Korean Assoc Learner-Centered Curric Instr, 25(1), 35-52. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2025.25.1.35
Mateo, J. D. (2024). Path Analysis of Grit, Self-Efficacy, Self-Regulation, and Science Academic Performance in Online Learning. Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies, 50(10), 299-314. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajess/2024/v50i101621
Noronha, A. P. P., Dias-Viana, J. L., & Cavallaro, A. P. O. (2024). The Influence of Grit on Life Satisfaction of Brazilian Undergraduate Students: Academic Adaptation as a Mediator. Frontiers in psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1331259
Norouzi, N. (2024). The Effect of Future Perspective Training on Academic Hope, Psychological Well-being, Goal Orientation, and Time Perspective in Eleventh-Grade Male Students Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz].
Obeng, P., Srem‐Sai, M., Salifu, I., Amoadu, M., Arthur, F., Agormedah, E. K., Hagan, J. E., & Schack, T. (2025). Linking Students' Grit and Academic Engagement: Mediating Role of Academic Motivation and Self‐regulated Learning. British Educational Research Journal. https://doi.org/10.1002/berj.4185
Panahi, G., Ardouni, T., & Kazemi, S. (2023). The Impact of Academic Aspiration on Academic Hope Through the Mediating Role of Academic Optimism in Students. Educational Psychology Studies, 20(50), 20-33. https://jeps.usb.ac.ir/article_7822.html
Raeisi, R. (2025). The Effectiveness of Hope Training on the Academic Motivation, Academic Hardiness, and Academic Hope of Second-grade Elementary School Students in Chelgerd. The 7th National Conference of Professional Research in Psychology and Counseling with a Teacher's Perspective,
Rahmani, M., Namvar, H., & Hashemi Razini, H. (2024). The Effectiveness of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on Executive Functions and Academic Procrastination of Children with Sluggish Cognitive Tempo. Journal of Psychological Dynamics in Mood Disorders (PDMD), 2(4), 82-90. https://doi.org/10.22034/pdmd.2024.434756.1038
Soleimani, M., Ghadampour, E., & Abbasi, M. (2023). A Feasibility Study of Education Based on Successful Academic Identity on Academic Persistence and Academic Well-being. Rooyesh-e Ravanshenasi Journal (Growth of Psychology), 12(12), 33-42.
Tammeh, B., Dortaj, F., Seadatee Shamir, A., & Farokhi, N. (2025). Developing a Structural Model for Academic Buoyancy based on Motivational Factors and Mediator Roles of Grit, Mental Toughness, and Control. Educational Psychology, 20(74), 7-32. https://journals.atu.ac.ir/article_18473.html
Tang, L., & Zhu, X. (2024). Academic self-efficacy, grit, and teacher support as predictors of psychological well-being of Chinese EFL students. Frontiers in psychology, 14, 1332909. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1332909
Torres, J., Chen, D., & Peixoto, B. (2025). Locus of Control and Its Relationship with Motivation: Mediated by Grit. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS). https://doi.org/10.61838/
Uribe-Moreno, M. E., Medina-Arboleda, I. F., Rincón, A. G., & Moreno, S. E. C. (2024). Alternative Grit Models: Explorations Into the Psychometric Properties of Grit-S and Academic Performance. International Journal of Educational Psychology, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.17583/ijep.12297