Predicting Adolescent Risk-Taking Behavior from Sensation Seeking and Peer Pressure
Keywords:
Adolescent risk-taking behavior, Sensation seeking, Peer pressure, Predictors, Nigerian adolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the predictive roles of sensation seeking and peer pressure in adolescent risk-taking behavior among Nigerian adolescents.
Methods and Materials: This descriptive-correlational research included 350 adolescents selected via convenience sampling from secondary schools in urban and semi-urban areas of Nigeria, with the sample size determined by Morgan and Krejcie’s sampling table. Participants completed the Adolescent Risk-Taking Questionnaire (ARQ) by Gullone et al. (2000), the Brief Sensation Seeking Scale (BSSS-8) by Hoyle et al. (2002), and the Resistance to Peer Influence Scale (RPI) by Steinberg and Monahan (2007). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlations, and multivariate linear regression via SPSS-27.
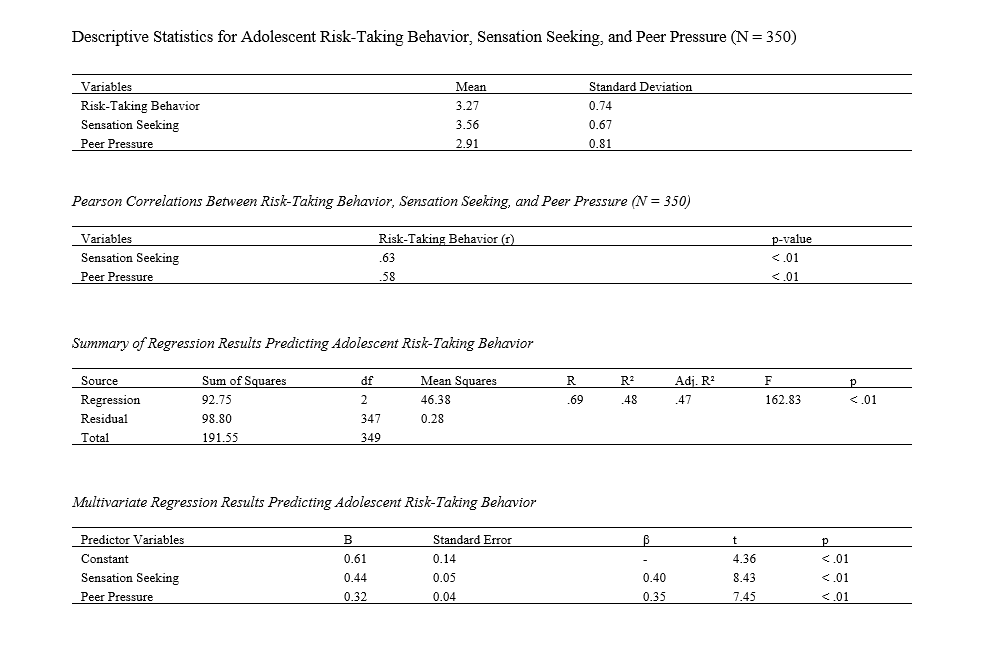
Findings: Descriptive analysis showed moderate levels of adolescent risk-taking behavior (M = 3.27, SD = 0.74), high sensation seeking (M = 3.56, SD = 0.67), and moderate peer pressure (M = 2.91, SD = 0.81). Correlation analysis revealed significant positive relationships between risk-taking behavior and sensation seeking (r = .63, p < .01), as well as peer pressure (r = .58, p < .01). Regression analysis indicated that sensation seeking and peer pressure significantly predicted adolescent risk-taking behavior (F(2,347) = 162.83, p < .01), jointly explaining 48% of its variance (R² = .48). Sensation seeking (β = 0.40, t = 8.43, p < .01) and peer pressure (β = 0.35, t = 7.45, p < .01) were both significant positive predictors.
Conclusion: This study confirms that both sensation seeking and peer pressure strongly predict adolescent risk-taking behaviors among Nigerian adolescents, highlighting the combined impact of individual predispositions and social influences. Interventions designed to reduce adolescent risk-taking should simultaneously address internal traits such as sensation seeking, and external factors, particularly peer pressure, to effectively mitigate adverse outcomes associated with adolescent risk behaviors.
Downloads
References
Bao, Y., Chen, Y., Liang, A., & Zhang, W. (2023). Impact of Parent-Child Relationship on Adolescent Risk-Taking Behavior: The Mediating Role of School Connectedness. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 8, 1976-1982. https://doi.org/10.54097/ehss.v8i.4627
Braams, B. R., Rijn, R. v., Leijser, T., & Dekkers, T. J. (2025). The Upside of ADHD-related Risk-Taking: Adolescents With ADHD Report a Higher Likelihood of Engaging in Prosocial Risk-Taking Behavior Than Typically Developing Adolescents. Journal of Attention Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1177/10870547251321882
Dai, J., Kwon, S. J., Prinstein, M. J., Telzer, E. H., & Lindquist, K. A. (2023). Neural Similarity in Nucleus Accumbens During Decision‐making for the Self and a Best Friend: Links to Adolescents' Self‐reported Susceptibility to Peer Influence and Risk Taking. Human Brain Mapping, 44(10), 3972-3985. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.26317
Defoe, I. N., Rap, S., & Römer, D. (2022). Adolescents’ Own Views on Their Risk Behaviors, and the Potential Effects of Being Labeled as Risk-Takers: A Commentary and Review. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.945775
Dou, K., Wang, L., Cheng, D. L., Li, Y., & Zhang, M. C. (2022). Longitudinal Association Between Poor Parental Supervision and Risk‐taking Behavior: The Role of Self‐control and School Climate. Journal of adolescence, 94(4), 525-537. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12043
Dou, K., Zhang, M. C., & Liang, Y. (2020). Adolescents’ Future Negative Time Perspective and Risk-Taking Behaviors: The Roles of Coping Styles and Self-Control. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/rgcts
Jia, X., Zhu, H., Sun, G., Meng, H., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Socioeconomic Status and Risk-Taking Behavior Among Chinese Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Psychological Capital and Self-Control. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.760968
Junaid, S., Batool, S. S., Nazir, R., & Nayyar, A. (2025). Relationship Between Peer Pressure and Risk Taking Behavior Among Adolescents: Moderating Role of Family Functioning. Res. J. Social Affairs, 3(1), 121-128. https://doi.org/10.71317/rjsa.003.01.0056
Keyzers, A., Weiler, L. M., Haddock, S. A., & Doty, J. (2019). Family Problem-Solving and Attachment Quality: Associations With Adolescent Risk-Taking Behavior. Journal of Youth Development, 14(1), 70-92. https://doi.org/10.5195/jyd.2019.637
Li, P., & Ma, J. (2025). The Influence of Parent-Child Relationship on Prosocial Risk-Taking Behavior in Adolescents: Understanding the Chain Mediating Role of Perceived Social Support and Psychological Capital. Journal of Educational Research and Policies, 7(2), 41-45. https://doi.org/10.53469/jerp.2025.07(02).08
Liang, Z., Dou, K., Li, J. B., Wang, Y., & Nie, Y. (2022). Linking Self-Control to Negative Risk-Taking Behavior Among Chinese Late Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Model. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(13), 7646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137646
Liu, L., Wang, N., & Tian, L. (2019). The Parent-Adolescent Relationship and Risk-Taking Behaviors Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Self-Control. Frontiers in psychology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00542
Lomakin, D. (2019). ECDP_2019_Deviant Behavior and Risk-Taking Among Adolescents. https://doi.org/10.13140/rg.2.2.21938.35528
Lu, H., & Fu, G. (2022). The Effect of Alexithymia on Adolescent Risk-Taking Behavior. International Journal of Humanities Social Sciences and Education, 9(8), 20-28. https://doi.org/10.20431/2349-0381.0908002
Maciejewski, D., Lauharatanahirun, N., Herd, T., Lee, J., Deater‐Deckard, K., King‐Casas, B., & Kim‐Spoon, J. (2018). Neural Cognitive Control Moderates the Association Between Insular Risk Processing and Risk-Taking Behaviors via Perceived Stress in Adolescents. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 30, 150-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2018.02.005
Maepa, M. P., & Ntshalintshali, T. (2020). Family Structure and History of Childhood Trauma: Associations With Risk-Taking Behavior Among Adolescents in Swaziland. Frontiers in Public Health, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.563325
Moreira, J. F. G., & Telzer, E. H. (2017). Family Conflict Shapes How Adolescents Take Risks When Their Family Is Affected. Developmental science, 21(4). https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12611
Nagel, M. (2019). Neurobiology of Risk Taking and Impulsivity. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119171492.wecad361
Nie, Y., Wang, G., Pei, C., Wang, L., & Dou, K. (2022). The Association Between Peer Victimization and Risk-Taking Behavior Among Chinese Adolescents: Testing a Moderated Mediation Model. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(21), 14198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114198
Peeters, M., Oldehinkel, T., & Vollebergh, W. (2017). Behavioral Control and Reward Sensitivity in Adolescents’ Risk Taking Behavior: A Longitudinal TRAILS Study. Frontiers in psychology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00231
Salas-Rodríguez, J., Jacinto, L. G., Hombrados‐Mendieta, I., & Pino‐Brunet, N. d. (2022). Applying an Evolutionary Approach of Risk-Taking Behaviors in Adolescents. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.694134
Siraj, R., Najam, B., & Ghazal, S. (2021). Sensation Seeking, Peer Influence, and Risk-Taking Behavior in Adolescents. Education Research International, 2021, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8403024
Siriphadung, S. (2019). Intergenerational Transmission of Religiosity and the Reduction of Thai Adolescent Risk Behaviors. Journal of Population and Social Studies, 27(2), 139-152. https://doi.org/10.25133/jpssv27n2.009
Thomas, S. A., Jain, A., Wilson, T., Deros, D. E., Jacobs, I., Dunn, E., Aldao, A., Stadnik, R., & Reyes, A. D. L. (2019). Moderated Mediation of the Link Between Parent-Adolescent Conflict and Adolescent Risk-Taking: The Role of Physiological Regulation and Hostile Behavior in an Experimentally Controlled Investigation. Journal of psychopathology and behavioral assessment, 41(4), 699-715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-019-09747-w
Tian, Y. (2024). Risk Taking in Adolescents and Relevant Factors. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 40, 54-59. https://doi.org/10.54097/3kh7q066
Wasserman, R., Anderson, B. J., & Schwartz, D. D. (2017). Illness-Specific Risk-Taking in Adolescence: A Missing Piece of the Nonadherence Puzzle for Youth With Type 1 Diabetes? Diabetes Spectrum, 30(1), 3-10. https://doi.org/10.2337/ds15-0060
丁, 紫. (2023). The Influence and Mechanism of Adolescent Risk-Taking Behavior. Advances in Psychology, 13(01), 76-84. https://doi.org/10.12677/ap.2023.131011
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








